State of the Art in Gold Nanoparticle Synthesisation via Pulsed Laser Ablation in Liquid and Its Characterisation for Molecular Imaging: A Review
- PMID: 35160822
- PMCID: PMC8838486
- DOI: 10.3390/ma15030875
State of the Art in Gold Nanoparticle Synthesisation via Pulsed Laser Ablation in Liquid and Its Characterisation for Molecular Imaging: A Review
Abstract
With recent advances in nanotechnology, various nanomaterials have been used as drug carriers in molecular imaging for the treatment of cancer. The unique physiochemical properties and biocompatibility of gold nanoparticles have developed a breakthrough in molecular imaging, which allows exploration of gold nanoparticles in drug delivery for diagnostic purpose. The conventional gold nanoparticles synthetisation methods have limitations with chemical contaminations during the synthesisation process and the use of higher energy. Thus, various innovative approaches in gold nanoparticles synthetisation are under development. Recently, studies have been focused on the development of eco-friendly, non-toxic, cost-effective and simple gold nanoparticle synthesisation. The pulsed laser ablation in liquid (PLAL) technique is a versatile synthetic and convincing technique due to its high efficiency, eco-friendly and facile method to produce gold nanoparticle. Therefore, this study aimed to review the eco-friendly gold nanoparticle synthesisation method via the PLAL method and to characterise the gold nanoparticles properties for molecular imaging. This review paper provides new insight to understand the PLAL technique in producing gold nanoparticles and the PLAL parameters that affect gold nanoparticle properties to meet the desired needs in molecular imaging.
Keywords: characterisation; gold nanoparticle; molecular imaging; pulsed laser ablation in liquid; synthesisation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
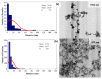
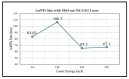

References
-
- Sengani M., Grumezescu A.M., Rajeswari V.D. Recent trends and methodologies in gold nanoparticle synthesis—A prospective review on drug delivery aspect. OpenNano. 2017;2:37–46. doi: 10.1016/j.onano.2017.07.001. - DOI
-
- Mohazzab B.F., Jaleh B., Nasrollahzadeh M., Issaabadi Z., Varma R.S. Laser ablation-assisted synthesis of GO/TiO2/Au nanocomposite: Applications in K3[Fe(CN)6] and Nigrosin reduction. Mol. Catal. 2019;473:110401. doi: 10.1016/j.mcat.2019.110401. - DOI
-
- Hernández-Maya M., Rivera-Quintero P., Ospina R., Quintero-Orozco J.H., García-Castro A.C. Ablation energy, water volume and ablation time: Gold nanoparticles obtained through by pulsed laser ablation in liquid. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2019;1386 doi: 10.1088/1742-6596/1386/1/012062. - DOI
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

