Recent Advances in Synthesis and Degradation of Lignin and Lignin Nanoparticles and Their Emerging Applications in Nanotechnology
- PMID: 35160893
- PMCID: PMC8838035
- DOI: 10.3390/ma15030953
Recent Advances in Synthesis and Degradation of Lignin and Lignin Nanoparticles and Their Emerging Applications in Nanotechnology
Abstract
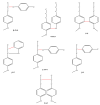
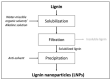
Lignin is an important commercially produced polymeric material. It is used extensively in both industrial and agricultural activities. Recently, it has drawn much attention from the scientific community. It is abundantly present in nature and has significant application in the production of biodegradable materials. Its wide usage includes drug delivery, polymers and several forms of emerging lignin nanoparticles. The synthesis of lignin nanoparticles is carried out in a controlled manner. The traditional manufacturing techniques are costly and often toxic and hazardous to the environment. This review article highlights simple, safe, climate-friendly and ecological approaches to the synthesis of lignin nanoparticles. The changeable, complex structure and recalcitrant nature of lignin makes it challenging to degrade. Researchers have discovered a small number of microorganisms that have developed enzymatic and non-enzymatic metabolic pathways to use lignin as a carbon source. These microbes show promising potential for the biodegradation of lignin. The degradation pathways of these microbes are also described, which makes the study of biological synthesis much easier. However, surface modification of lignin nanoparticles is something that is yet to be explored. This review elucidates the recent advances in the biodegradation of lignin in the ecological system. It includes the current approaches, methods for modification, new applications and research for the synthesis of lignin and lignin nanoparticles. Additionally, the intricacy of lignin's structure, along with its chemical nature, is well-described. This article will help increase the understanding of the utilization of lignin as an economical and alternative-resource material. It will also aid in the minimization of solid waste arising from lignin.
Keywords: degradation; lignin; ligninolytic enzymes; nanobioremediation; nanoparticles.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Recent updates on green synthesis of lignin nanoparticle and its potential applications in modern biotechnology.Crit Rev Biotechnol. 2024 Aug;44(5):774-794. doi: 10.1080/07388551.2023.2229512. Epub 2023 Jul 16. Crit Rev Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 37455422 Review.
-
Lignin nanoparticles enter the scene: A promising versatile green tool for multiple applications.Biotechnol Adv. 2021 Mar-Apr;47:107685. doi: 10.1016/j.biotechadv.2020.107685. Epub 2020 Dec 29. Biotechnol Adv. 2021. PMID: 33383155 Review.
-
Technological advancement in the synthesis and applications of lignin-based nanoparticles derived from agro-industrial waste residues: A review.Int J Biol Macromol. 2020 Nov 15;163:1828-1843. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.09.076. Epub 2020 Sep 17. Int J Biol Macromol. 2020. PMID: 32950524 Review.
-
Recent advances in biological activities of lignin and emerging biomedical applications: A short review.Int J Biol Macromol. 2022 May 31;208:819-832. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2022.03.182. Epub 2022 Mar 29. Int J Biol Macromol. 2022. PMID: 35364209 Review.
-
Lignin Nanoparticles: Transforming Environmental Remediation.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2024 Sep 23;14(18):1541. doi: 10.3390/nano14181541. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39330697 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Bioethanol production from alkali-pretreated rice straw: effects on fermentation yield, structural characterization, and ethanol analysis.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023 Aug 3;11:1243856. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2023.1243856. eCollection 2023. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 37600305 Free PMC article.
-
Do Lignin Nanoparticles Pave the Way for a Sustainable Nanocircular Economy? Biostimulant Effect of Nanoscaled Lignin in Tomato Plants.Plants (Basel). 2024 Jul 4;13(13):1839. doi: 10.3390/plants13131839. Plants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38999679 Free PMC article.
-
Nanostructured Antibiotics and Their Emerging Medicinal Applications: An Overview of Nanoantibiotics.Antibiotics (Basel). 2022 May 25;11(6):708. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics11060708. Antibiotics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35740115 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Green and Low-Cost Natural Lignocellulosic Biomass-Based Carbon Fibers-Processing, Properties, and Applications in Sports Equipment: A Review.Polymers (Basel). 2022 Jun 26;14(13):2591. doi: 10.3390/polym14132591. Polymers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35808637 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Isolation of delignifying bacteria and optimization of microbial pretreatment of biomass for bioenergy.Biotechnol Lett. 2024 Apr;46(2):183-199. doi: 10.1007/s10529-023-03463-y. Epub 2024 Jan 22. Biotechnol Lett. 2024. PMID: 38252364
References
-
- Arapova O.V., Chistyakov A.V., Tsodikov M.V., Moiseev I.I. Lignin as a Renewable Resource of Hydrocarbon Products and Energy Carriers (A Review) Pet. Chem. 2020;60:227–243. doi: 10.1134/S0965544120030044. - DOI
-
- Arora A., Nandal P., Singh J., Verma M.L. Nanobiotechnological advancements in lignocellulosic biomass pretreatment. Mater. Sci. Energy Technol. 2020;3:308–318. doi: 10.1016/j.mset.2019.12.003. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

