Evaluation of the Antimicrobial Effect of Graphene Oxide Fiber on Fish Bacteria for Application in Aquaculture Systems
- PMID: 35160912
- PMCID: PMC8840572
- DOI: 10.3390/ma15030966
Evaluation of the Antimicrobial Effect of Graphene Oxide Fiber on Fish Bacteria for Application in Aquaculture Systems
Abstract
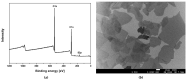
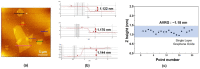
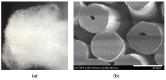
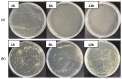
The growing importance of the domestic aquaculture industry has led not only to its continuous development and expansion but also to an increase in the production of wastewater containing pathogenic microorganisms and antibiotic-resistant bacteria. As the existing water purification facilities have a high initial cost of construction, operation, and maintenance, it is necessary to develop an economical solution. Graphene oxide (GO) is a carbon-based nanomaterial that is easy to manufacture, inexpensive and has excellent antimicrobial properties. In this study, the antimicrobial effect of GO polyester fibers on seven species of fish pathogenic bacteria was analyzed to evaluate their effectiveness in water treatment systems and related products. As a result of incubating GO polyester fibers with seven types of fish pathogenic bacteria for 1, 6, and 12 h, there was no antimicrobial effect in Vibrio harveyi, V. scopthalmi, and Edwardsiella tarda. In contrast, GO fibers showed antimicrobial effects of more than 99% against A. hydrophila, S. parauberis, S. iniae, and P. piscicola, suggesting the potential use of GO fibers in water treatment systems.
Keywords: fish bacterial disease; graphene oxide; graphene oxide polyester fiber; water treatment.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Biofilm formation of pathogenic bacteria isolated from aquatic animals.Arch Microbiol. 2022 Dec 24;205(1):36. doi: 10.1007/s00203-022-03332-8. Arch Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 36565346 Review.
-
Antimicrobial activity of essential oil of Eucalyptus globulus against fish pathogenic bacteria.Lab Anim Res. 2016 Jun;32(2):87-90. doi: 10.5625/lar.2016.32.2.87. Epub 2016 Jun 24. Lab Anim Res. 2016. PMID: 27382376 Free PMC article.
-
A multivalent killed whole-cell vaccine induces effective protection against Edwardsiella tarda and Vibrio anguillarum.Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2011 Oct;31(4):595-9. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2011.06.025. Epub 2011 Jul 13. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21763772
-
Construction and evaluation of a live vaccine against Edwardsiella tarda and Vibrio harveyi: laboratory vs. mock field trial.Vaccine. 2011 May 31;29(24):4081-5. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2011.04.025. Epub 2011 Apr 21. Vaccine. 2011. PMID: 21514342
-
Exploring the roles of phytobiotics in relieving the impacts of Edwardsiella tarda infection on fish: a mini-review.Front Vet Sci. 2023 Jul 5;10:1149514. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2023.1149514. eCollection 2023. Front Vet Sci. 2023. PMID: 37476823 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Ecotoxicity Assessment of Graphene Oxides Using Test Organisms from Three Hierarchical Trophic Levels to Evaluate Their Potential Environmental Risk.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2023 Oct 28;13(21):2858. doi: 10.3390/nano13212858. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37947703 Free PMC article.
-
Management and Mitigation of Vibriosis in Aquaculture: Nanoparticles as Promising Alternatives.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Aug 8;24(16):12542. doi: 10.3390/ijms241612542. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37628723 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Lee B.U., Yun S.H., Ji J.H., Bae G.N. Inactivation of S. epidermidis, B. subtilis, and E. coli bacteria bioaerosols deposited on a filter utilizing airborne silver nanoparticles. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2008;18:176–182. - PubMed
-
- Lin C.Y., Li C.S. Control effectiveness of ultraviolet germicidal irradiation on bioaerosols. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2002;36:474–478. doi: 10.1080/027868202753571296. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

