The Surface Conditions and Composition of Titanium Alloys in Implantology: A Comparative Study of Dental Implants of Different Brands
- PMID: 35160961
- PMCID: PMC8840750
- DOI: 10.3390/ma15031018
The Surface Conditions and Composition of Titanium Alloys in Implantology: A Comparative Study of Dental Implants of Different Brands
Abstract
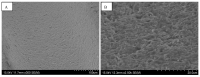
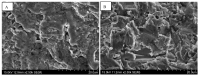
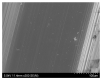
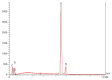
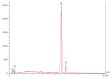
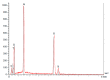
The success of titanium dental implants depends on their osseointegration into the bone, which is determined by the composition and surface properties of the implant in close contact with the bone. There is a wide variety of implants on the market. Is it possible to identify the implant with the best composition and surface topography for optimal osseointegration? To this aim, 13 brands of dental implants from nine distinct manufacturers have been selected and their composition and surface topography determined. The obtained results show differences between these implants, in this case, the Ssk averages of the three measurements performed on each implant were positive, or 0.4 (0.1-0.8), indicating that the roughness of all implants analyzed was primarily textured and not flat. Like Sa, we found the highest Sdr for implants subjected only to sandblasting. In addition, only the ALS-active® implant had a modified microstructure on its surface. However, analysis of the NANOTITE implant surface revealed a 1.40% presence of calcium which we consider too low to have an effect on bone formation around the implant. As a result, we have also highlighted the lack of a recognized independent standard for dental implant surface conditions and the lack of independent quality control vis-à-vis manufacturers. Of all the surface types studied, none proved more satisfactory than another.
Keywords: composition; implants; sandblasting; surface; titanium.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

