Water-Soluble Starch-Based Copolymers Synthesized by Electron Beam Irradiation: Physicochemical and Functional Characterization
- PMID: 35161009
- PMCID: PMC8839537
- DOI: 10.3390/ma15031061
Water-Soluble Starch-Based Copolymers Synthesized by Electron Beam Irradiation: Physicochemical and Functional Characterization
Abstract
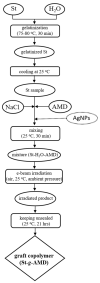
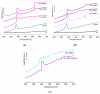
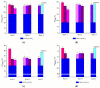
Modification of natural polymers for applications in the treatment of waste and surface waters is a continuous concern of researchers and technologists in close relation to the advantages they provide as related to classical polymeric flocculants. In this work, copolymers of starch-graft-polyacrylamide (St-g-PAM) were synthesized by electron beam irradiation used as the free radical initiator by applying different irradiation doses and dose rates. St-g-PAM loaded with ex situ prepared silver nanoparticles was also synthesized by using an accelerated electron beam. The graft copolymers were characterized by chemical analysis, rheology, and differential scanning calorimetry (DSC). The results showed that the level of grafting (monomer conversion coefficient and residual monomer concentration), intrinsic viscosity and thermal behavior (thermodynamic parameters) were influenced by the irradiation dose, dose rate and presence of silver nanoparticles. The flocculation performances of the synthesized copolymers were also tested on water from the meat industry in experiments at the laboratory level. In the coagulation-flocculation process, the copolymer aqueous solutions showed good efficiency to improve different water quality indicators.
Keywords: flocculant; grafting copolymerization; intrinsic viscosity; polysaccharide; radiation; thermal behavior.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Synthesis of Natural-Inspired Materials by Irradiation: Data Mining from the Perspective of Their Functional Properties in Wastewater Treatment.Materials (Basel). 2023 Mar 28;16(7):2686. doi: 10.3390/ma16072686. Materials (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37048979 Free PMC article.
-
Microwave assisted synthesis of polyacrylamide grafted starch (St-g-PAM) and its applicability as flocculant for water treatment.Int J Biol Macromol. 2011 Jan 1;48(1):106-11. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2010.10.004. Epub 2010 Oct 15. Int J Biol Macromol. 2011. PMID: 20951725
-
Synthesis and Characterization of Novel Hybrid Flocculants Based on Potato Starch Copolymers with Hollow Carbon Spheres.Materials (Basel). 2021 Mar 18;14(6):1498. doi: 10.3390/ma14061498. Materials (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33803841 Free PMC article.
-
Preparation of cashew gum-based flocculants by microwave- and ultrasound-assisted methods.Int J Biol Macromol. 2018 Feb;107(Pt B):1550-1558. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2017.09.118. Epub 2017 Oct 8. Int J Biol Macromol. 2018. PMID: 29020653
-
Grafting Starch with Acrylic Acid and Fenton's Initiator: The Selectivity Challenge.Polymers (Basel). 2024 Jan 16;16(2):255. doi: 10.3390/polym16020255. Polymers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38257054 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Synthesis of Natural-Inspired Materials by Irradiation: Data Mining from the Perspective of Their Functional Properties in Wastewater Treatment.Materials (Basel). 2023 Mar 28;16(7):2686. doi: 10.3390/ma16072686. Materials (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37048979 Free PMC article.
-
Dual Modification of Starch by Physical Methods Based on Corona Electrical Discharge and Ionizing Radiation: Synergistic Impact on Rheological Behavior.Foods. 2022 Aug 17;11(16):2479. doi: 10.3390/foods11162479. Foods. 2022. PMID: 36010483 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Peng B., Yao Z., Wang X., Crombeen M., Sweeney D.G., Tam K.C. Cellulose-based materials in wastewater treatment of petroleum industry. Green Energy Environ. 2020;5:37–49. doi: 10.1016/j.gee.2019.09.003. - DOI
-
- Nayak A.K., Hasnain M.S., Aminabhavi T.M. Drug delivery using interpenetrating polymeric networks of natural polymers: A recent update. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2021;66:102915. doi: 10.1016/j.jddst.2021.102915. - DOI
Grants and funding
- Romanian National Nucleu Program LAPLAS VI-16N/2019/Ministerul Cercetării și Inovării
- National Interest Facilities of the National Institute for Lasers, Plasma and Radiation Phys-ics-Electron Accelerators Laboratory/Ministerul Cercetării și Inovării
- grant/Unitatea Executiva Pentru Finantarea Invatamantului Superior a Cercetarii Dezvoltarii si Inovarii
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

