Identification and Functional Characterization of FLOWERING LOCUS T in Platycodon grandiflorus
- PMID: 35161306
- PMCID: PMC8840131
- DOI: 10.3390/plants11030325
Identification and Functional Characterization of FLOWERING LOCUS T in Platycodon grandiflorus
Abstract
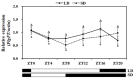
Platycodon grandiflorus roots have been used as a foodstuff and traditional medicine for thousands of years in East Asia. In order to increase the root development of P. grandiflorus, cultivators removed the inflorescences, suggesting the possible negative effect of flowering on root development. This indicates that the genetic improvement of P. grandiflorus by late flowering is a potential approach to increase productivity. However, nothing is known about key genes integrating multiple flowering pathways in P. grandiflorus. In order to fill this gap, we identified potential homologs of the FLOWERING LOCUS T (FT) gene in P. grandiflorus. The alignment with other FT members and phylogenetic analysis revealed that the P. grandiflorus FT (PlgFT) protein contains highly conserved functional domains and belongs to the FT-like clade. The expression analysis revealed spatial variations in the transcription of PlgFT in different organs. In addition, the expression level of PlgFT was increased by high temperature but not by photoperiodic light input signals, presumably due to lacking the CONSTANS binding motif in its promoter region. Furthermore, PlgFT induced early flowering upon its overexpression in P. grandiflorus, suggesting the functional role of PlgFT in flowering. Taken together, we functionally characterized PlgFT as a master regulator of P. grandiflorus flowering under inductive high temperature, which will serve as an important target gene for improving the root productivity.
Keywords: CONSTANS; FLOWERING LOCUS T; Platycodon grandiflorus; temperature.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

