Colorimetric and Electrochemical Screening for Early Detection of Diabetes Mellitus and Diabetic Retinopathy-Application of Sensor Arrays and Machine Learning
- PMID: 35161465
- PMCID: PMC8839630
- DOI: 10.3390/s22030718
Colorimetric and Electrochemical Screening for Early Detection of Diabetes Mellitus and Diabetic Retinopathy-Application of Sensor Arrays and Machine Learning
Abstract
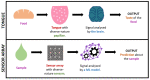
In this review, a selection of works on the sensing of biomarkers related to diabetes mellitus (DM) and diabetic retinopathy (DR) are presented, with the scope of helping and encouraging researchers to design sensor-array machine-learning (ML)-supported devices for robust, fast, and cost-effective early detection of these devastating diseases. First, we highlight the social relevance of developing systematic screening programs for such diseases and how sensor-arrays and ML approaches could ease their early diagnosis. Then, we present diverse works related to the colorimetric and electrochemical sensing of biomarkers related to DM and DR with non-invasive sampling (e.g., urine, saliva, breath, tears, and sweat samples), with a special mention to some already-existing sensor arrays and ML approaches. We finally highlight the great potential of the latter approaches for the fast and reliable early diagnosis of DM and DR.
Keywords: diabetes mellitus; diabetic retinopathy; early detection and diagnosis; glucose sensing; machine learning; point-of-care; screening; sensor arrays.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

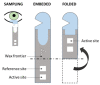

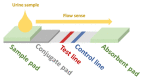
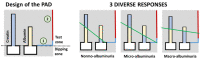
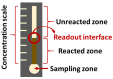
References
-
- Van Waateringe R.P., Fokkens B.T., Slagter S.N., Van Der Klauw M.M., Van Vliet-Ostaptchouk J.V., Graaff R., Paterson A.D., Smit A.J., Lutgers H.L., Wolffenbuttel B.H.R. Skin autofluorescence predicts incident type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease and mortality in the general population. Diabetologia. 2019;62:269–280. doi: 10.1007/s00125-018-4769-x. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

