Blockchain Based Solutions to Mitigate Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) Attacks in the Internet of Things (IoT): A Survey
- PMID: 35161838
- PMCID: PMC8840306
- DOI: 10.3390/s22031094
Blockchain Based Solutions to Mitigate Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) Attacks in the Internet of Things (IoT): A Survey
Abstract
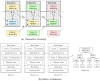
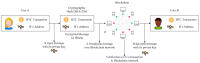
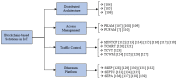
Internet of Things (IoT) devices are widely used in many industries including smart cities, smart agriculture, smart medical, smart logistics, etc. However, Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks pose a serious threat to the security of IoT. Attackers can easily exploit the vulnerabilities of IoT devices and control them as part of botnets to launch DDoS attacks. This is because IoT devices are resource-constrained with limited memory and computing resources. As an emerging technology, Blockchain has the potential to solve the security issues in IoT. Therefore, it is important to analyse various Blockchain-based solutions to mitigate DDoS attacks in IoT. In this survey, a detailed survey of various Blockchain-based solutions to mitigate DDoS attacks in IoT is carried out. First, we discuss how the IoT networks are vulnerable to DDoS attacks, its impact over IoT networks and associated services, the use of Blockchain as a potential technology to address DDoS attacks, in addition to challenges of Blockchain implementation in IoT. We then discuss various existing Blockchain-based solutions to mitigate the DDoS attacks in the IoT environment. Then, we classify existing Blockchain-based solutions into four categories i.e., Distributed Architecture-based solutions, Access Management-based solutions, Traffic Control-based solutions and the Ethereum Platform-based solutions. All the solutions are critically evaluated in terms of their working principles, the DDoS defense mechanism (i.e., prevention, detection, reaction), strengths and weaknesses. Finally, we discuss future research directions that can be explored to design and develop better Blockchain-based solutions to mitigate DDoS attacks in IoT.
Keywords: blockchain; distributed denial of service (DDoS) attacks; internet of things (IoT); mitigation of DDoS attacks.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors do not declare any conflict of interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
DDoS Attack Prevention for Internet of Thing Devices Using Ethereum Blockchain Technology.Sensors (Basel). 2022 Sep 8;22(18):6806. doi: 10.3390/s22186806. Sensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36146163 Free PMC article.
-
Adaptive Machine Learning Based Distributed Denial-of-Services Attacks Detection and Mitigation System for SDN-Enabled IoT.Sensors (Basel). 2022 Mar 31;22(7):2697. doi: 10.3390/s22072697. Sensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35408312 Free PMC article.
-
Software-Defined-Networking-Based One-versus-Rest Strategy for Detecting and Mitigating Distributed Denial-of-Service Attacks in Smart Home Internet of Things Devices.Sensors (Basel). 2024 Aug 3;24(15):5022. doi: 10.3390/s24155022. Sensors (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39124069 Free PMC article.
-
Systematic Literature Review of IoT Botnet DDOS Attacks and Evaluation of Detection Techniques.Sensors (Basel). 2024 Jun 1;24(11):3571. doi: 10.3390/s24113571. Sensors (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38894365 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Taxonomy of DDoS Attack Mitigation Approaches Featured by SDN Technologies in IoT Scenarios.Sensors (Basel). 2020 May 29;20(11):3078. doi: 10.3390/s20113078. Sensors (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32485943 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Hybridization of synergistic swarm and differential evolution with graph convolutional network for distributed denial of service detection and mitigation in IoT environment.Sci Rep. 2024 Dec 28;14(1):30868. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-81116-4. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39730632 Free PMC article.
-
Enhancing Cancer Care through Blockchain Technology.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2025 Apr 1;26(4):1139-1153. doi: 10.31557/APJCP.2025.26.4.1139. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2025. PMID: 40302065 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Review of the Authentication Techniques for Internet of Things Devices in Smart Cities: Opportunities, Challenges, and Future Directions.Sensors (Basel). 2025 Mar 7;25(6):1649. doi: 10.3390/s25061649. Sensors (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40292695 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Critical Cybersecurity Analysis and Future Research Directions for the Internet of Things: A Comprehensive Review.Sensors (Basel). 2023 Apr 19;23(8):4117. doi: 10.3390/s23084117. Sensors (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37112457 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Blockchain-Modeled Edge-Computing-Based Smart Home Monitoring System with Energy Usage Prediction.Sensors (Basel). 2023 Jun 1;23(11):5263. doi: 10.3390/s23115263. Sensors (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37299993 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rghioui A., Oumnad A. Internet of things: Surveys for measuring human activities from everywhere. Int. J. Electr. Comput. Eng. 2017;7:2474–2482. doi: 10.11591/ijece.v7i5.pp2474-2482. - DOI
-
- IHS Market The Internet of Things: A Moment, Not a Market. [(accessed on 18 November 2021)]. Available online: https://cdn.ihs.com/www/pdf/IoT_ebook.pdf.
-
- Li S., Tryfonas T., Li H. The Internet of things: A security point of view. Internet Res. 2016;26:337–359. doi: 10.1108/IntR-07-2014-0173. - DOI
-
- Rashmi D., Devadkar K. Understanding DDoS attack & its effect in cloud environment. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2015;49:202–210.
-
- Mohammad M., Abdolee R., Tazekand B.M. On the convergence of blockchain and Internet of Things (IoT) technologies. arXiv. 20191904.01936
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

