A High-Performance Deep Neural Network Model for BI-RADS Classification of Screening Mammography
- PMID: 35161903
- PMCID: PMC8838754
- DOI: 10.3390/s22031160
A High-Performance Deep Neural Network Model for BI-RADS Classification of Screening Mammography
Abstract
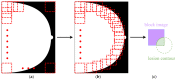
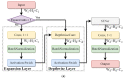
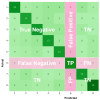
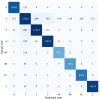
Globally, the incidence rate for breast cancer ranks first. Treatment for early-stage breast cancer is highly cost effective. Five-year survival rate for stage 0-2 breast cancer exceeds 90%. Screening mammography has been acknowledged as the most reliable way to diagnose breast cancer at an early stage. Taiwan government has been urging women without any symptoms, aged between 45 and 69, to have a screening mammogram bi-yearly. This brings about a large workload for radiologists. In light of this, this paper presents a deep neural network (DNN)-based model as an efficient and reliable tool to assist radiologists with mammographic interpretation. For the first time in the literature, mammograms are completely classified into BI-RADS categories 0, 1, 2, 3, 4A, 4B, 4C and 5. The proposed model was trained using block-based images segmented from a mammogram dataset of our own. A block-based image was applied to the model as an input, and a BI-RADS category was predicted as an output. At the end of this paper, the outperformance of this work is demonstrated by an overall accuracy of 94.22%, an average sensitivity of 95.31%, an average specificity of 99.15% and an area under curve (AUC) of 0.9723. When applied to breast cancer screening for Asian women who are more likely to have dense breasts, this model is expected to give a higher accuracy than others in the literature, since it was trained using mammograms taken from Taiwanese women.
Keywords: breast imaging reporting and data system (BI-RADS); deep learning; deep neural network (DNN); image classification; screening mammography.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures







Similar articles
-
A deep learning method for classifying mammographic breast density categories.Med Phys. 2018 Jan;45(1):314-321. doi: 10.1002/mp.12683. Epub 2017 Dec 22. Med Phys. 2018. PMID: 29159811 Free PMC article.
-
A New Computer-Aided Diagnosis System with Modified Genetic Feature Selection for BI-RADS Classification of Breast Masses in Mammograms.Biomed Res Int. 2020 May 11;2020:7695207. doi: 10.1155/2020/7695207. eCollection 2020. Biomed Res Int. 2020. PMID: 32462017 Free PMC article.
-
Understanding Clinical Mammographic Breast Density Assessment: a Deep Learning Perspective.J Digit Imaging. 2018 Aug;31(4):387-392. doi: 10.1007/s10278-017-0022-2. J Digit Imaging. 2018. PMID: 28932980 Free PMC article.
-
Breast Mass Detection and Classification Using Machine Learning Approaches on Two-Dimensional Mammogram: A Review.Crit Rev Biomed Eng. 2024;52(4):41-60. doi: 10.1615/CritRevBiomedEng.2024051166. Crit Rev Biomed Eng. 2024. PMID: 38780105 Review.
-
[Analysis of mammograms performed in a public imaging center in Santiago, Metropolitan Region Chile 2008-2018].Rev Med Chil. 2022 Jun;150(6):727-735. doi: 10.4067/S0034-98872022000600727. Rev Med Chil. 2022. PMID: 37906907 Review. Spanish.
Cited by
-
CNN-Based Cross-Modality Fusion for Enhanced Breast Cancer Detection Using Mammography and Ultrasound.Tomography. 2024 Dec 12;10(12):2038-2057. doi: 10.3390/tomography10120145. Tomography. 2024. PMID: 39728907 Free PMC article.
-
Benign and Malignant Breast Tumor Classification in Ultrasound and Mammography Images via Fusion of Deep Learning and Handcraft Features.Entropy (Basel). 2023 Jun 28;25(7):991. doi: 10.3390/e25070991. Entropy (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37509938 Free PMC article.
-
Neural Network-Based Mammography Analysis: Augmentation Techniques for Enhanced Cancer Diagnosis-A Review.Bioengineering (Basel). 2025 Feb 24;12(3):232. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering12030232. Bioengineering (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40150696 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neural Network in the Analysis of the MR Signal as an Image Segmentation Tool for the Determination of T1 and T2 Relaxation Times with Application to Cancer Cell Culture.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jan 13;24(2):1554. doi: 10.3390/ijms24021554. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36675075 Free PMC article.
-
Artificial intelligence in mammography: a systematic review of the external validation.Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2024 Sep 4;46:e-rbgo71. doi: 10.61622/rbgo/2024rbgo71. eCollection 2024. Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2024. PMID: 39380589 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cancer Registry Annual Report, 2018 Taiwan. Health Promotion Administration, Ministry of Health and Welfare, Taiwan, December 2020. [(accessed on 6 October 2021)]; Available online: https://www.hpa.gov.tw/EngPages/Detail.aspx?nodeid=1061&pid=6069.
-
- Chen Y.P., Lu Y.W., Yang C.C. Breast cancer trend in Taiwan. MOJ Women’s Health. 2017;6:376–379.
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

