A Review on Planted (l, d) Motif Discovery Algorithms for Medical Diagnose
- PMID: 35161949
- PMCID: PMC8838483
- DOI: 10.3390/s22031204
A Review on Planted (l, d) Motif Discovery Algorithms for Medical Diagnose
Abstract
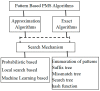
Personalized diagnosis of chronic disease requires capturing the continual pattern across the biological sequence. This repeating pattern in medical science is called "Motif". Motifs are the short, recurring patterns of biological sequences that are supposed signify some health disorder. They identify the binding sites for transcription factors that modulate and synchronize the gene expression. These motifs are important for the analysis and interpretation of various health issues like human disease, gene function, drug design, patient's conditions, etc. Searching for these patterns is an important step in unraveling the mechanisms of gene expression properly diagnose and treat chronic disease. Thus, motif identification has a vital role in healthcare studies and attracts many researchers. Numerous approaches have been characterized for the motif discovery process. This article attempts to review and analyze fifty-four of the most frequently found motif discovery processes/algorithms from different approaches and summarizes the discussion with their strengths and weaknesses.
Keywords: evolutionary approach; hashing; local search approach; mismatch tree; probabilistic approach; search tree; suffix tree; tries.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Waterman M.S. An Introduction to Computational Biology: Maps, Sequences and Genomes. Chapman & Hall; London, UK: CRC Press; Boca Raton, FL, USA: 1995. Interdisciplinary Statistics.
-
- Chauhan R., Agarwal P. A Review Appling Genetic Algorithm for Motif Discovery. Int. J. Comput. Technol. Appl. 2012;3:1510–1515.
-
- Pradhan M. Master’s Thesis. San Jose State University; San Jose, CA, USA: Dec, 2008. [(accessed on 17 November 2021)]. Motif Discovery in Biological Sequences. Available online: http://scholarworks.sjsu.edu/etd_projects/106.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources