Recurrent Neural Network Based Link Quality Prediction for Fluctuating Low Power Wireless Links
- PMID: 35161954
- PMCID: PMC8838954
- DOI: 10.3390/s22031212
Recurrent Neural Network Based Link Quality Prediction for Fluctuating Low Power Wireless Links
Abstract
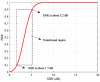
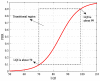
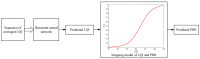
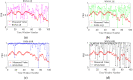
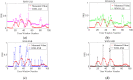
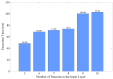
One of the main methods for link quality prediction is to predict the physical layer parameters first, and then evaluate the link quality based on the mapping models between such parameters and packet reception ratio (PRR). However, existing methods often ignore the temporal correlations of physical layer parameter series and rarely consider the influence of link fluctuations, which lead to more errors under moderate and sudden changed links with larger fluctuations. In view of these problems, this paper proposes a more effective link quality prediction method RNN-LQI, which adopts Recurrent Neural Network (RNN) to predict the Link Quality Indicator (LQI) series, and then evaluates the link quality according to the fitting model of LQI and PRR. This method accurately mines the inner relationship among LQI series with the help of short-term memory characteristics of RNN and effectively deals with link fluctuations by taking advantage of the higher resolution of LQI in the transitional region. Compared with similar methods, RNN-LQI proves to be better under different link qualities. Especially under moderate and sudden changed links with larger fluctuations, the prediction error reduces at least by 14.51% and 13.37%, respectively. Therefore, the proposed method is more suitable for low power wireless links with more fluctuations.
Keywords: link quality indicator; link quality prediction; low power wireless links; recurrent neural network; temporal correlation; time series.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Link Investigation of IEEE 802.15.4 Wireless Sensor Networks in Forests.Sensors (Basel). 2016 Jun 27;16(7):987. doi: 10.3390/s16070987. Sensors (Basel). 2016. PMID: 27355957 Free PMC article.
-
Environmental Impacts on Hardware-Based Link Quality Estimators in Wireless Sensor Networks.Sensors (Basel). 2020 Sep 17;20(18):5327. doi: 10.3390/s20185327. Sensors (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32957643 Free PMC article.
-
Prediction of the motion of chest internal points using a recurrent neural network trained with real-time recurrent learning for latency compensation in lung cancer radiotherapy.Comput Med Imaging Graph. 2021 Jul;91:101941. doi: 10.1016/j.compmedimag.2021.101941. Epub 2021 May 28. Comput Med Imaging Graph. 2021. PMID: 34265553
-
Water quality prediction based on recurrent neural network and improved evidence theory: a case study of Qiantang River, China.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2019 Jul;26(19):19879-19896. doi: 10.1007/s11356-019-05116-y. Epub 2019 May 15. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2019. PMID: 31093910
-
SS-RNN: A Strengthened Skip Algorithm for Data Classification Based on Recurrent Neural Networks.Front Genet. 2021 Oct 13;12:746181. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2021.746181. eCollection 2021. Front Genet. 2021. PMID: 34721533 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Dynamic Heterogeneous User Generated Contents-Driven Relation Assessment via Graph Representation Learning.Sensors (Basel). 2022 Feb 11;22(4):1402. doi: 10.3390/s22041402. Sensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35214304 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chen C., Wang Z., Li W., Chen H., Mei Z., Yuan W., Tao L., Zhao Y., Huang G., Mei Y., et al. Novel flexible material-based unobtrusive and wearable body sensor networks for vital sign monitoring. IEEE Sens. J. 2019;19:8502–8513. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2018.2887107. - DOI
-
- Baccour N., Koubaa A., Mottola L., Youssef H., Boano C.A., Alves M. Radio link quality estimation in wireless sensor networks: A survey. ACM Trans. Sens. Netw. 2012;8:1–33. doi: 10.1145/2240116.2240123. - DOI
-
- Woo A., Culler D. Technical Report UCB/CSD-03-1270. EECS Department, University of California; Berkeley, CA, USA: 2003. Evaluation of efficient link reliability estimators for low-power wireless networks.
-
- Liu W., Xia Y., Luo R. FaLQE: Fluctuation adaptive link quality estimator for wireless sensor networks. Commun. Comput. Inf. Sci. 2019;1101:48–60.
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- 2017YFC0822404/National Key R&D Program of China
- 62031017/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 61601069/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- KJQN202001110/Scientific and Technological Research Program of Chongqing Municipal Education Commission
- KJQN201901136/Scientific and Technological Research Program of Chongqing Municipal Education Commission
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

