Respiratory Monitoring by Ultrafast Humidity Sensors with Nanomaterials: A Review
- PMID: 35161997
- PMCID: PMC8838830
- DOI: 10.3390/s22031251
Respiratory Monitoring by Ultrafast Humidity Sensors with Nanomaterials: A Review
Abstract
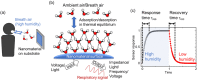
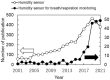
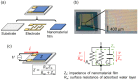
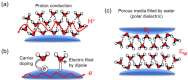
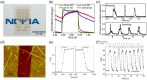
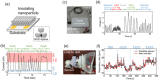
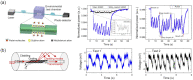
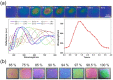
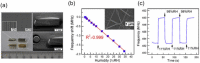
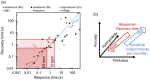
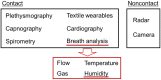
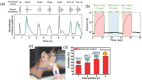
Respiratory monitoring is a fundamental method to understand the physiological and psychological relationships between respiration and the human body. In this review, we overview recent developments on ultrafast humidity sensors with functional nanomaterials for monitoring human respiration. Key advances in design and materials have resulted in humidity sensors with response and recovery times reaching 8 ms. In addition, these sensors are particularly beneficial for respiratory monitoring by being portable and noninvasive. We systematically classify the reported sensors according to four types of output signals: impedance, light, frequency, and voltage. Design strategies for preparing ultrafast humidity sensors using nanomaterials are discussed with regard to physical parameters such as the nanomaterial film thickness, porosity, and hydrophilicity. We also summarize other applications that require ultrafast humidity sensors for physiological studies. This review provides key guidelines and directions for preparing and applying such sensors in practical applications.
Keywords: fast response; humidity sensor; nanomaterial; physiological monitoring; respiratory monitoring.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
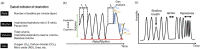


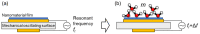


References
-
- Yuan G., Drost A.N., Mclvor R.A. Respiratory Rate and Breathing Pattern. McMaster Univ. Med. J. 1990;10:23–25.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

