Obesity and Thyroid Cancer Risk: An Update
- PMID: 35162142
- PMCID: PMC8834607
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph19031116
Obesity and Thyroid Cancer Risk: An Update
Abstract
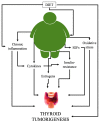
Thyroid cancer (TC) is the most common endocrine malignancy worldwide and its incidence has increased dramatically in recent years. In parallel, the prevalence of overweight and obesity has also increased, suggesting a possible link between these two diseases. Indeed, low-grade chronic inflammation, altered cytokine levels, insulin resistance, oxidative stress, and hormonal changes that occur in obese patients are all factors that contribute to the occurrence and growth of TC. In this review, the most recent evidence supporting the potential role of the mechanisms linking obesity to TC will be discussed.
Keywords: cytokines; estrogens; insulin; insulin resistance; obesity; overweight; oxidative stress; risk factors; thyroid carcinoma.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Agate L., Lorusso L., Elisei R. New and old knowledge on differentiated thyroid cancer epidemiology and risk factors. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2012;35:3–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

