Stages of Change in Dairy Intake among Older Adults: Application of the Transtheoretical Model
- PMID: 35162169
- PMCID: PMC8835001
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph19031146
Stages of Change in Dairy Intake among Older Adults: Application of the Transtheoretical Model
Abstract
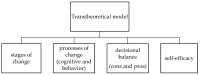
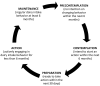
Adequate dairy product intake can reduce the risk of chronic disease, mortality, low quality of life, and healthcare expenditure. However, the insufficient consumption of dairy products is a serious issue in Eastern societies. To the authors' knowledge, few studies have explored dairy intake among Taiwanese older adults, especially using the transtheoretical model. The study aims were to address the following unknowns: (i) the distribution of dairy product intake behavior on stages of change (SOC); (ii) differences in variables (intake knowledge (IK), intake cons (IC), intake pros (IP), and intake self-efficacy (ISE)) among SOCs; (iii) discriminative abilities of variables on SOCs; and (iv) predictive ability of variables (IK, IC, IP, and ISE) for dairy product intake behavior on SOC for older adults. An explorative cross-sectional study was conducted to collect data from northern Taiwan using a questionnaire. A total of 342 older adults were recruited. Data were analyzed using multivariate analysis of variance, discriminant analysis, and multiple linear regression. There was a significant difference between the variables and SOCs. There was a better discriminant among the five SOCs. Dairy product intake behaviors were significantly associated with knowledge and self-efficacy in the pre-action stage, and with cons, pros, and self-efficacy in the post-action stage. In conclusion, appropriate nutritional empowerment could benefit older adults by improving dairy intake among the different SOCs.
Keywords: dairy product intake; older adults; self-efficacy; stages of change (SOC); transtheoretical model.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Stages of dairy product consumption among Iranian female high school students based on transtheoretical model: The case of osteoporosis prevention.Nutr Health. 2024 Sep;30(3):565-572. doi: 10.1177/02601060221131207. Epub 2022 Oct 12. Nutr Health. 2024. PMID: 36221981
-
How Ready Are Young Adults to Participate in Community Service? An Application of the Transtheoretical Model of Behavior Change.Am J Health Promot. 2022 Jan;36(1):64-72. doi: 10.1177/08901171211034742. Epub 2021 Jul 23. Am J Health Promot. 2022. PMID: 34296641
-
The Effects of Empowerment Education on Daily Dairy Intake in Community-Dwelling of Older Asian Women.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021 Apr 27;18(9):4659. doi: 10.3390/ijerph18094659. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021. PMID: 33925699 Free PMC article.
-
Transtheoretical Model for Physical Activity in Older Adults: Systematic Review.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020 Dec 11;17(24):9262. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17249262. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020. PMID: 33322327 Free PMC article.
-
Calcium intake trends and health consequences from childhood through adulthood.J Am Coll Nutr. 2003 Oct;22(5):340-56. doi: 10.1080/07315724.2003.10719317. J Am Coll Nutr. 2003. PMID: 14559926 Review.
Cited by
-
A qualitative study to explore and identify reasons for dairy consumption and non-consumption among young adults (18-30 years old) in the UK and France.J Nutr Sci. 2024 Dec 6;13:e90. doi: 10.1017/jns.2024.78. eCollection 2024. J Nutr Sci. 2024. PMID: 39703898 Free PMC article.
-
The influence of health information attention and app usage frequency of older adults on persuasive strategies in mHealth education apps.Digit Health. 2023 Mar 30;9:20552076231167003. doi: 10.1177/20552076231167003. eCollection 2023 Jan-Dec. Digit Health. 2023. PMID: 37021126 Free PMC article.
-
Is it advisable for Asians to drink milk, especially those at risk of osteoporosis?Front Nutr. 2025 Jun 25;12:1586623. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2025.1586623. eCollection 2025. Front Nutr. 2025. PMID: 40635901 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Pan W. 2013–2016 Nutrition and Health Survey in Taiwan. [(accessed on 14 October 2021)];2019 Available online: https://www.hpa.gov.tw/EngPages/Detail.aspx?nodeid=1077&pid=6201. (In Chinese)
-
- Farvid M.S., Malekshah A.F., Pourshams A., Poustchi H., Sepanlou S.G., Sharafkhah M., Khoshnia M., Farvid M., Abnet C.C., Kamangar F., et al. Dairy Food Intake and All-Cause, Cardiovascular Disease, and Cancer Mortality: The Golestan Cohort Study. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2017;185:697–711. doi: 10.1093/aje/kww139. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chang C.-F., Yeh Y.-L., Chang H.-Y., Tsai S.-H., Wang J.-Y. Prevalence and Risk Factors of Sarcopenia among Older Adults Aged ≥ 65 Years Admitted to Daycare Centers of Taiwan: Using AWGS 2019 Guidelines. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health. 2021;18:8299. doi: 10.3390/ijerph18168299. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous