Consumer Acceptance toward Functional Foods: A Scoping Review
- PMID: 35162240
- PMCID: PMC8835010
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph19031217
Consumer Acceptance toward Functional Foods: A Scoping Review
Abstract
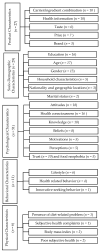
Chronic diseases (e.g., heart disease, cancer, diabetes) are of major public concern. Such chronic diseases are often caused by a dietary pattern characterized as relatively high in fat, refined sugar, salt, and cholesterol. Societal interest in consuming healthy foods and the demand for healthy food products have increased significantly. As a result, functional foods have gained significant research attention in the food health and technology innovations field. To date, many studies have investigated the factors that may predict consumer acceptance of functional foods, and a wide range of influential factors have been reported. However, studies conducted in different contexts pose challenges to gaining a clear understanding of the factors influencing consumer acceptance. Therefore, the purpose of our scoping review was to synthesize the possible determinants of consumer acceptance toward functional foods and provide a resource that describes global trends regarding consumers' functional foods behavior. We identified 75 articles published with varying populations around the globe that empirically investigated consumers' acceptance of functional foods. We identified and categorized a wide range of determinants related to consumer acceptance of different types of functional foods. The five categories of determinants were product characteristics, socio-demographic characteristics, psychological characteristics, behavioral characteristics, and physical characteristics. Each of the determinants were more fully described by sub-determinants in our scoping review. These determinants should be considered and used by leaders and scientists in product development to aid decision making and, ultimately, the successful launch of novel functional foods.
Keywords: consumer acceptance; functional foods; scoping review.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Department of Health and Human Services Dietary Guidelines for Americans 2015–2020. [(accessed on 17 December 2021)]; Available online: https://health.gov/our-work/nutrition-physical-activity/dietary-guidelin....
-
- Bagchi D. Nutraceutical and Functional Food Regulations in the United States and around the World. 3rd ed. Academic Press; London, UK: 2019.
-
- Bigliardi B., Galati F. Innovation trends in the food industry: The case of functional foods. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2013;31:118–129. doi: 10.1016/j.tifs.2013.03.006. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials