Recommendations to Enhance Parental Involvement and Adolescent Participation in Physical Activity
- PMID: 35162356
- PMCID: PMC8835355
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph19031333
Recommendations to Enhance Parental Involvement and Adolescent Participation in Physical Activity
Abstract
Background: Adolescents are influenced by external factors which may impact their level of physical activity. Parents require specific strategies to become involved and to increase physical activity participation in adolescence.
Objective: Thus, the current study aimed to design recommendations to increase physical activity participation and parental involvement.
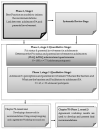
Methods: The current study forms part of a broader mixed-method study in which the results of the phases and stages of the pre-studies informed the current study. Thus, the current study uses an agreement workshop to develop recommendations with stakeholder and expert input in two rounds. Participants were invited to participate in the current study n = 100, and n = 65 participated in round one. Round two consisted of n = 20 experts invited to an agreement workshop, with n = 11 attending and making an input on the final recommendations. Therefore, experts and parents in the field of parenting, physical activity, and physical education, were invited to participate in the study rounds. After each round, the responses from the panellists were collated, interpreted, and developed into a framework for recommendations using thematic analysis. Themes were generated and refined using an agreement format.
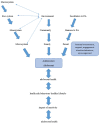
Results: After results from the stages and phases were consolidated and refined, six themes and 51 sub-themes were identified in a framework for recommendations. The framework was further refined using expert input and the final recommendations were derived using an agreement or agreement. Thus, with input from experts input through the agreement workshop, the findings were discussed, refined, and drafted into recommendations. Agreement and agreement were achieved on six broad recommendations and fifty-one sub-themes. The final recommendations were presented in the current study to increase parental involvement and physical activity in adolescents.
Discussion: Recommendations and physical activity resources were developed and are presented as a form of support to parents and adolescents. The recommendations are intended as a source of unbiased information for parents to become more involved and for adolescents to increase physical activity participation.
Keywords: adolescence; adolescent; parental involvement; physical activity; physical inactivity; recommendations.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that no conflict of interest exists.
Figures
Similar articles
-
PARENTS 2 study: consensus report for parental engagement in the perinatal mortality review process.Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2019 Aug;54(2):215-224. doi: 10.1002/uog.20139. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2019. PMID: 30294945 Free PMC article.
-
What do parents think of using informational videos to support recruitment for parenting trials? A qualitative study.Trials. 2021 Dec 4;22(1):872. doi: 10.1186/s13063-021-05826-0. Trials. 2021. PMID: 34863256 Free PMC article.
-
Sustained participation in community-based physical activity by adolescents with cerebral palsy: a qualitative study.Disabil Rehabil. 2019 Dec;41(25):3043-3051. doi: 10.1080/09638288.2018.1486466. Epub 2018 Jul 10. Disabil Rehabil. 2019. PMID: 29987965
-
Reasons for non-participation in a parental program concerning underage drinking: a mixed-method study.BMC Public Health. 2009 Dec 21;9:478. doi: 10.1186/1471-2458-9-478. BMC Public Health. 2009. PMID: 20025743 Free PMC article.
-
Physical activity and family-based obesity treatment: a review of expert recommendations on physical activity in youth.Clin Obes. 2018 Feb;8(1):68-79. doi: 10.1111/cob.12230. Epub 2017 Dec 10. Clin Obes. 2018. PMID: 29224232 Review.
Cited by
-
The impact of parental psychological control on adolescents' physical activity: the mediating role of self-control and the moderating role of psychological capital.Front Psychol. 2025 May 14;16:1501720. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2025.1501720. eCollection 2025. Front Psychol. 2025. PMID: 40438754 Free PMC article.
-
How Does Adolescents' Usage of Social Media Affect Their Dietary Satisfaction?Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Mar 18;19(6):3621. doi: 10.3390/ijerph19063621. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 35329307 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cozett C., Bassett S.H., Leach L. Factors influencing participation in physical activity among 11–13-year-old school children in the Western Cape, South Africa. Afr. J. Phys. Act. Health Sci. (AJPHES) 2016;22:1100–1107.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical