Effect of Knee Orthosis Pressure Variation on Muscle Activities during Sit-to-Stand Motion in Patients with Knee Osteoarthritis
- PMID: 35162362
- PMCID: PMC8835671
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph19031341
Effect of Knee Orthosis Pressure Variation on Muscle Activities during Sit-to-Stand Motion in Patients with Knee Osteoarthritis
Abstract
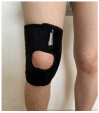
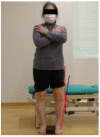
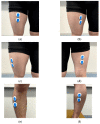
It is yet not known whether the variation in knee orthotics pressure would lead to changes in muscle activity during-sit-to-stand postural transition in patients with knee osteoarthritis (OA). Participants in this analytical study were patients with knee OA. The research design was a cross-sectional study. They were enrolled in the study through a sample of convenience method. The primary outcome measure was surface electromyography for measuring muscle activity while changing knee orthotics pressure during sit-to-stand motion. Data were summarized with mean and standard deviation while Friedman's test was performed for multiple comparison of variables, at a significance level of p = 0.05. Seven elderly patients with knee osteoarthritis (mean age 71.4 ± 11.8 years) participated in the study. Moderate orthotics (7.3 mmHg) led to a significant increase in the percentage maximum voluntary contraction (MVC) of tibialis anterior compared to that obtained without orthotics. Rectus femoris, vastus medialis, vastus lateralis, and biceps femoris tended to increase the % MVC with an increase in wearing pressure. It was therefore concluded that the muscle activity during sit-to-stand motion could be increased in patients with knee osteoarthritis by wearing flexible orthotics with varying pressure.
Keywords: knee orthosis; knee osteoarthritis; muscle activity; sit-to-stand motion; wearing pressure.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Postural Balance in Individuals With Knee Osteoarthritis During Stand-to-Sit Task.Front Hum Neurosci. 2021 Nov 3;15:760960. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2021.760960. eCollection 2021. Front Hum Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34803639 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamic Frequency Analyses of Lower Extremity Muscles during Sit-To-Stand Motion for the Patients with Knee Osteoarthritis.PLoS One. 2016 Jan 25;11(1):e0147496. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0147496. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 26807578 Free PMC article.
-
Kinematics and knee muscle activation during sit-to-stand movement in women with knee osteoarthritis.Clin Biomech (Bristol). 2015 Jul;30(6):599-607. doi: 10.1016/j.clinbiomech.2015.03.025. Epub 2015 Mar 30. Clin Biomech (Bristol). 2015. PMID: 25846323
-
Neuromuscular efficiency during sit to stand movement in women with knee osteoarthritis.J Electromyogr Kinesiol. 2011 Oct;21(5):689-94. doi: 10.1016/j.jelekin.2011.05.006. J Electromyogr Kinesiol. 2011. PMID: 21689947
-
The influence of knee varus and valgus on quadriceps muscle activity changes induced by stretching and kneeling.J Electromyogr Kinesiol. 2022 Apr;63:102636. doi: 10.1016/j.jelekin.2022.102636. Epub 2022 Jan 21. J Electromyogr Kinesiol. 2022. PMID: 35093685
References
-
- Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare Overview of the 2016 National Life Basic Survey. [(accessed on 9 June 2021)]. Available online: http://www.mhlw.go.jp/toukei/saikin/hw/k-tyosa/k-tyosa16/index.html.
-
- Yoshimura N., Muraki S., Oka H., Mabuchi A., En-Yo Y., Yoshida M., Saika A., Yoshida H., Suzuki T., Yamamoto S., et al. Prevalence of knee osteoarthritis, lumbar spondylosis and osteoporosis in Japanese men and women. The research on osteoarthritis/osteoporosis against Disability (ROAD) J. Bone Miner. Metab. 2009;27:620–628. doi: 10.1007/s00774-009-0080-8. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Anan M., Tokuda K., Kito N., Shinkoda K. Kinematic analysis of chair-standing movement in knee osteoarthritis. Phys. Ther. Sci. 2010;25:755–760.
-
- Fujii T., Toda H., Ishikawa H., Kito N., Sasaki H. Age-related changes in muscle function that affect the production of internal hip extension moments during standing up. Physiother. Sci. 2013;28:463–468.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

