Single Nucleotide Polymorphism of TWIST2 May Be a Modifier for the Association between High-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol and Blood Lead (Pb) Level
- PMID: 35162374
- PMCID: PMC8834775
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph19031352
Single Nucleotide Polymorphism of TWIST2 May Be a Modifier for the Association between High-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol and Blood Lead (Pb) Level
Abstract
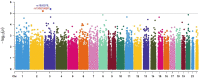
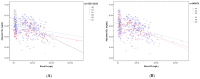
The association between lead (Pb) exposure and lower high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) was reported; however, the mechanism was unclear. Our purpose was to investigate the association of Pb, lipid profile, and to study the associated SNPs using a genome-wide association study (GWAS). A total of 511 participants were recruited to check blood Pb levels, lipid profile, and genotypes with Taiwan Biobank version 2.0 (TWB2). Our main result shows that HDL-C was significantly negatively associated with blood Pb levels, adjusted for gender, body mass index (BMI), and potential confounders. In addition, via the TWB2 GWAS, only two SNPs were found, including rs150813626 (single-nucleotide variation in the TWIST2 gene on chromosome 2), and rs1983079 (unclear SNP on chromosome 3). Compared to the rs150813626 GG carriers, the AA and AG carriers were significantly and negatively associated with HDL-C. We analyzed the interaction of rs150813626 SNP and blood Pb, and the HDL-C was consistently and negatively associated with blood Pb, male, BMI, and the rs150813626 AA and AG carriers. Moreover, the rs150813626 AA and blood Pb interaction was significantly and positively associated with HDL-C. In conclusion, the SNPs rs150813626 and rs1983079 were significantly associated with HDL-C in Pb-exposed workers. Furthermore, the interaction of rs150813626 AA and blood Pb had a positive influence on HDL-C. TWIST may inhibit osteoblast maturation, which might relate to bone Pb deposition and calcium metabolism. The mechanism needs more investigation in the future.
Keywords: Taiwan biobank; genome-wide association study; high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C); lead (Pb); single nucleotide polymorphism.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Apolipoprotein C-I Polymorphism and Its Association with Serum Lipid Levels and Longevity in the Bama Population.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2017 May 9;14(5):505. doi: 10.3390/ijerph14050505. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2017. PMID: 28486432 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide association analysis of total cholesterol and high-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels using the Framingham heart study data.BMC Med Genet. 2010 Apr 6;11:55. doi: 10.1186/1471-2350-11-55. BMC Med Genet. 2010. PMID: 20370913 Free PMC article.
-
Association of MYLIP rs3757354 SNP and several environmental factors with serum lipid levels in the Guangxi Bai Ku Yao and Han populations.Lipids Health Dis. 2012 Oct 29;11:141. doi: 10.1186/1476-511X-11-141. Lipids Health Dis. 2012. PMID: 23107276 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-Wide Association Study on Adiponectin-Mediated Suppression of HDL-C Levels in Taiwanese Individuals Identifies Functional Haplotypes in CDH13.Genes (Basel). 2021 Oct 7;12(10):1582. doi: 10.3390/genes12101582. Genes (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34680977 Free PMC article.
-
Interactions of several single nucleotide polymorphisms and high body mass index on serum lipid traits.Biofactors. 2013 May-Jun;39(3):315-25. doi: 10.1002/biof.1073. Epub 2013 Jan 28. Biofactors. 2013. PMID: 23355348
Cited by
-
Single and combined associations of blood lead and essential metals with serum lipid profiles in community-dwelling adults.Front Nutr. 2023 Apr 14;10:1129169. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2023.1129169. eCollection 2023. Front Nutr. 2023. PMID: 37125027 Free PMC article.
-
Associations of Metal Mixtures with Lipid Profiles: Exploring the Mediating Role of Testosterone in a Cross-Sectional Study.Biol Trace Elem Res. 2025 Jul 25. doi: 10.1007/s12011-025-04745-4. Online ahead of print. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2025. PMID: 40711747
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

