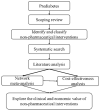
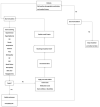
Effectiveness and Cost-Effectiveness of Non-Pharmacological Interventions among Chinese Adults with Prediabetes: A Protocol for Network Meta-Analysis and CHIME-Modeled Cost-Effectiveness Analysis
- PMID: 35162645
- PMCID: PMC8835234
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph19031622
Effectiveness and Cost-Effectiveness of Non-Pharmacological Interventions among Chinese Adults with Prediabetes: A Protocol for Network Meta-Analysis and CHIME-Modeled Cost-Effectiveness Analysis
Abstract
Patients with prediabetes who are at a high risk of progressing to diabetes are recommended early-stage intervention, according to guidelines. Non-pharmacological interventions are effective and cost-effective for glycemic control compared with medicines. We aim to explore which non-pharmacological interventions have the greatest potential effectiveness, cost-effectiveness, and feasibility in community-based diabetes management in China. We will perform a systematic review and network meta-analysis to compare the effectiveness of included non-pharmacological interventions, then use Chinese Hong Kong Integrated Modeling and Evaluation (CHIME) to model the yearly incidence of complications, costs, and health utility for the lifetime. Published studies (only randomized controlled trials (RCTs) and cluster RCTs with at least one study arm of any non-pharmacological intervention) will be retrieved and screened using several databases. Primary outcomes included blood glucose, glycated hemoglobin, incidence of type 2 diabetes mellitus, and achievement of normoglycemia. Health utilities and cost parameters are to be calculated using a societal perspective and integrated into the modified CHIME model to achieve quality-adjusted life-year (QALY) estimates and lifetime costs. QALYs and incremental cost-effectiveness ratio will then be used to determine effectiveness and cost-effectiveness, respectively. Our study findings can inform improved diabetes management in countries with no intervention programs for these patients.
Keywords: China; Chinese Hong Kong Integrated Modeling and Evaluation; cost-effectiveness; non-pharmacological interventions; prediabetes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Adefovir dipivoxil and pegylated interferon alfa-2a for the treatment of chronic hepatitis B: a systematic review and economic evaluation.Health Technol Assess. 2006 Aug;10(28):iii-iv, xi-xiv, 1-183. doi: 10.3310/hta10280. Health Technol Assess. 2006. PMID: 16904047
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Smoking cessation medicines and e-cigarettes: a systematic review, network meta-analysis and cost-effectiveness analysis.Health Technol Assess. 2021 Oct;25(59):1-224. doi: 10.3310/hta25590. Health Technol Assess. 2021. PMID: 34668482
-
The effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of carmustine implants and temozolomide for the treatment of newly diagnosed high-grade glioma: a systematic review and economic evaluation.Health Technol Assess. 2007 Nov;11(45):iii-iv, ix-221. doi: 10.3310/hta11450. Health Technol Assess. 2007. PMID: 17999840
-
Drugs for preventing postoperative nausea and vomiting in adults after general anaesthesia: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Oct 19;10(10):CD012859. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012859.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. PMID: 33075160 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Cost-effectiveness and potential budget impact of non-pharmacological interventions for early management in prehypertensive people: an economic evaluation for China.BMC Public Health. 2023 Aug 11;23(1):1531. doi: 10.1186/s12889-023-16458-1. BMC Public Health. 2023. PMID: 37568086 Free PMC article.
References
-
- International Diabetes Federation . IDF Diabetes Atlas. 10th ed. International Diabetes Federation; Brussels, Belgium: 2021.
-
- World Health Organization . Global Report on Diabetes. World Health Organization; Geneva, Switzerland: 2016.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical