Simultaneous Heterotrophic Nitrification and Aerobic Denitrification of Water after Sludge Dewatering in Two Sequential Moving Bed Biofilm Reactors (MBBR)
- PMID: 35162866
- PMCID: PMC8834992
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph19031841
Simultaneous Heterotrophic Nitrification and Aerobic Denitrification of Water after Sludge Dewatering in Two Sequential Moving Bed Biofilm Reactors (MBBR)
Abstract
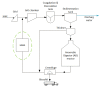
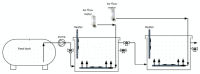
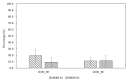
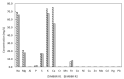
Water after sludge dewatering, also known as reject water from anaerobic digestion, is recycled back to the main wastewater treatment inlet in the wastewater treatment plant Porsgrunn, Norway, causing periodic process disturbance due to high ammonium of 568 (±76.7) mg/L and total chemical oxygen demand (tCOD) of 2825 (±526) mg/L. The main aim of this study was the simultaneous treatment of reject water ammonium and COD using two pilot-scale sequential moving bed biofilm reactors (MBBR) implemented in the main wastewater treatment stream. The two pilot MBBRs each had a working volume of 67.4 L. The biofilm carriers used had a protected surface area of 650 m2/m3 with a 60% filling ratio. The results indicate that the combined ammonia removal efficiency (ARE) in both reactors was 65.9%, while the nitrite accumulation rate (NAR) and nitrate production rate (NPR) were 80.2 and 19.8%, respectively. Over 28% of the reject water's tCOD was removed in both reactors. The heterotrophic nitrification and oxygen tolerant aerobic denitrification were the key biological mechanisms found for the ammonium removal in both reactors. The dominant bacterial family in both reactors was Alcaligenaceae, capable of simultaneous heterotrophic nitrification and denitrification. Moreover, microbial families that were found with equal potential for application of simultaneous heterotrophic nitrification and aerobic denitrification including Cloacamonaceae, Alcaligenaceae, Comamonadaceae, Microbacteriaceae, and Anaerolinaceae.
Keywords: biofilm; carriers; heterotrophic; reject water; sequencing.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Simultaneous nitrification and denitrification in continuous flow MBBR with novel surface-modified carriers.Environ Technol. 2021 Sep;42(23):3607-3617. doi: 10.1080/09593330.2020.1735526. Epub 2020 Mar 4. Environ Technol. 2021. PMID: 32097578
-
Simultaneous nitrification and denitrification in moving bed bioreactor and other biological systems.Bioprocess Biosyst Eng. 2021 Apr;44(4):635-652. doi: 10.1007/s00449-020-02475-6. Epub 2021 Jan 2. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng. 2021. PMID: 33387005 Review.
-
Comparison of the effects of salinity on microbial community structures and functions in sequencing batch reactors with and without carriers.Bioprocess Biosyst Eng. 2020 Dec;43(12):2175-2188. doi: 10.1007/s00449-020-02403-8. Epub 2020 Jul 13. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng. 2020. PMID: 32661564
-
The microbiome of two strategies for ammonia removal with the sequencing batch moving bed biofilm reactor treating cheese production wastewater.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2023 Dec 21;89(12):e0150723. doi: 10.1128/aem.01507-23. Epub 2023 Nov 27. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 38009922 Free PMC article.
-
Simultaneous nitrification-denitrification in biofilm systems for wastewater treatment: Key factors, potential routes, and engineered applications.Bioresour Technol. 2022 Oct;361:127702. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2022.127702. Epub 2022 Jul 26. Bioresour Technol. 2022. PMID: 35905872 Review.
Cited by
-
Development and Characterization of Ammonia Removal Moving Bed Biofilms for Landfill Leachate Treatment.Microorganisms. 2024 Nov 23;12(12):2404. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms12122404. Microorganisms. 2024. PMID: 39770607 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of media length on biofilms and nitrification in moving bed biofilm reactors.Biofilm. 2022 Oct 28;4:100091. doi: 10.1016/j.bioflm.2022.100091. eCollection 2022 Dec. Biofilm. 2022. PMID: 36389262 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Janus H.M., van der Roest H.F. Don’t reject the idea of treating reject water. Water Sci. Technol. 1997;35:27–34. doi: 10.2166/wst.1997.0351. - DOI
-
- Sivalingam V., Dinamarca C., Janka E., Kukankov S., Wang S., Bakke R. Effect of Intermittent Aeration in a Hybrid Vertical Anaerobic Biofilm Reactor (HyVAB) for Reject Water Treatment. Water. 2020;12:1151. doi: 10.3390/w12041151. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

