Culture Condition of Bone Marrow Stromal Cells Affects Quantity and Quality of the Extracellular Vesicles
- PMID: 35162938
- PMCID: PMC8834965
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23031017
Culture Condition of Bone Marrow Stromal Cells Affects Quantity and Quality of the Extracellular Vesicles
Abstract
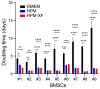
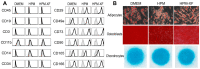
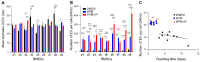
Extracellular vesicles (EVs) released by bone marrow stromal cells (BMSCs) have been shown to act as a transporter of bioactive molecules such as RNAs and proteins in the therapeutic actions of BMSCs in various diseases. Although EV therapy holds great promise to be a safer cell-free therapy overcoming issues related to cell therapy, manufacturing processes that offer scalable and reproducible EV production have not been established. Robust and scalable BMSC manufacturing methods have been shown to enhance EV production; however, the effects on EV quality remain less studied. Here, using human BMSCs isolated from nine healthy donors, we examined the effects of high-performance culture media that can rapidly expand BMSCs on EV production and quality in comparison with the conventional culture medium. We found significantly increased EV production from BMSCs cultured in the high-performance media without altering their multipotency and immunophenotypes. RNA sequencing revealed that RNA contents in EVs from high-performance media were significantly reduced with altered profiles of microRNA enriched in those related to cellular growth and proliferation in the pathway analysis. Given that pre-clinical studies at the laboratory scale often use the conventional medium, these findings could account for the discrepancy in outcomes between pre-clinical and clinical studies. Therefore, this study highlights the importance of selecting proper culture conditions for scalable and reproducible EV manufacturing.
Keywords: bone marrow stromal cells (BMSCs); culture condition; extracellular vesicles (EVs); miRNAs.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

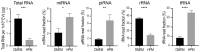
Similar articles
-
microRNA-148a-3p in extracellular vesicles derived from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells suppresses SMURF1 to prevent osteonecrosis of femoral head.J Cell Mol Med. 2020 Oct;24(19):11512-11523. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.15766. Epub 2020 Sep 1. J Cell Mol Med. 2020. PMID: 32871042 Free PMC article.
-
Bone marrow stromal and anterior cruciate ligament remnant cell co-culture-derived extracellular vesicles promote cell activity in both cell types.J Cell Mol Med. 2024 Sep;28(17):e70049. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.70049. J Cell Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 39219013 Free PMC article.
-
BMSC-derived extracellular vesicles intervened the pathogenic changes of scleroderma in mice through miRNAs.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021 Jun 5;12(1):327. doi: 10.1186/s13287-021-02400-y. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021. PMID: 34090522 Free PMC article.
-
The role of small extracellular vesicles in cerebral and myocardial ischemia-Molecular signals, treatment targets, and future clinical translation.Stem Cells. 2021 Apr;39(4):403-413. doi: 10.1002/stem.3329. Epub 2021 Jan 12. Stem Cells. 2021. PMID: 33432732 Review.
-
Manufacturing and characterization of extracellular vesicles from umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stromal cells for clinical testing.Cytotherapy. 2019 Jun;21(6):581-592. doi: 10.1016/j.jcyt.2018.12.006. Epub 2019 Apr 9. Cytotherapy. 2019. PMID: 30979664 Review.
Cited by
-
The proteomic landscape of extracellular vesicles derived from human intervertebral disc cells.JOR Spine. 2024 Nov 5;7(4):e70007. doi: 10.1002/jsp2.70007. eCollection 2024 Dec. JOR Spine. 2024. PMID: 39507593 Free PMC article.
-
CRISPR-dCas9 Activation of TSG-6 in MSCs Modulates the Cargo of MSC-Derived Extracellular Vesicles and Attenuates Inflammatory Responses in Human Intervertebral Disc Cells In Vitro.Cell Mol Bioeng. 2025 Feb 5;18(1):83-98. doi: 10.1007/s12195-025-00843-4. eCollection 2025 Feb. Cell Mol Bioeng. 2025. PMID: 39949490 Free PMC article.
-
Human amniotic fluid derived extracellular vesicles attenuate T cell immune response.Front Immunol. 2022 Nov 28;13:977809. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.977809. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36518766 Free PMC article.
-
Bioengineering extracellular vesicles: smart nanomaterials for bone regeneration.J Nanobiotechnology. 2023 Apr 27;21(1):137. doi: 10.1186/s12951-023-01895-2. J Nanobiotechnology. 2023. PMID: 37106449 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MSC-EV therapy for bone/cartilage diseases.Bone Rep. 2022 Nov 9;17:101636. doi: 10.1016/j.bonr.2022.101636. eCollection 2022 Dec. Bone Rep. 2022. PMID: 36389627 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Otsuru S., Desbourdes L., Guess A.J., Hofmann T.J., Relation T., Kaito T., Dominici M., Iwamoto M., Horwitz E.M. Extracellular vesicles released from mesenchymal stromal cells stimulate bone growth in osteogenesis imperfecta. Cytotherapy. 2018;20:62–73. doi: 10.1016/j.jcyt.2017.09.012. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Otsuru S., Gordon P.L., Shimono K., Jethva R., Marino R., Phillips C.L., Hofmann T.J., Veronesi E., Dominici M., Iwamoto M., et al. Transplanted bone marrow mononuclear cells and MSCs impart clinical benefit to children with osteogenesis imperfecta through different mechanisms. Blood. 2012;120:1933–1941. doi: 10.1182/blood-2011-12-400085. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

