The Role of Hydrogen Sulfide in Plant Roots during Development and in Response to Abiotic Stress
- PMID: 35162947
- PMCID: PMC8835357
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23031024
The Role of Hydrogen Sulfide in Plant Roots during Development and in Response to Abiotic Stress
Abstract
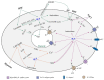
Hydrogen sulfide (H2S) is regarded as a "New Warrior" for managing plant stress. It also plays an important role in plant growth and development. The regulation of root system architecture (RSA) by H2S has been widely recognized. Plants are dependent on the RSA to meet their water and nutritional requirements. They are also partially dependent on the RSA for adapting to environment change. Therefore, a good understanding of how H2S affects the RSA could lead to improvements in both crop function and resistance to environmental change. In this review, we summarized the regulating effects of H2S on the RSA in terms of primary root growth, lateral and adventitious root formation, root hair development, and the formation of nodules. We also discussed the genes involved in the regulation of the RSA by H2S, and the relationships with other signal pathways. In addition, we discussed how H2S regulates root growth in response to abiotic stress. This review could provide a comprehensive understanding of the role of H2S in roots during development and under abiotic stress.
Keywords: auxin; heavy metal; hydrogen sulfide; nitric oxide; root growth; salt.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Balliu A., Zheng Y., Sallaku G., Fernández J.A., Gruda N.S., Tuzel Y. Environmental and cultivation factors affect the morphology, architecture and performance of root systems in soilless grown plants. Horticulturae. 2021;7:243. doi: 10.3390/horticulturae7080243. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

