Lifestyle Factors Involved in the Pathogenesis of Alopecia Areata
- PMID: 35162962
- PMCID: PMC8835065
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23031038
Lifestyle Factors Involved in the Pathogenesis of Alopecia Areata
Abstract
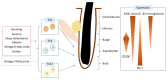
Alopecia areata is a representative inflammatory skin disease that is associated with various environmental stimuli. While psychological stress is believed to be a major pathogenetic trigger in alopecia areata, infants and newborns also suffer from the disease, suggesting the possible presence of other environmental factors. Daily lifestyle is well known to be involved in various inflammatory diseases and influences the severity of inflammatory skin diseases. However, only a limited number of studies have summarized these influences on alopecia areata. In this review article, we summarize lifestyle factor-related influences on the pathogenesis of alopecia areata and focus on environmental factors, such as smoking, alcohol consumption, sleep, obesity, fatty acids, and gluten consumption.
Keywords: Th1; Th17; Th2; alopecia areata; lifestyle factors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

