Emerging Insights on the Diverse Roles of Proprotein Convertase Subtilisin/Kexin Type 9 (PCSK9) in Chronic Liver Diseases: Cholesterol Metabolism and Beyond
- PMID: 35162992
- PMCID: PMC8834914
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23031070
Emerging Insights on the Diverse Roles of Proprotein Convertase Subtilisin/Kexin Type 9 (PCSK9) in Chronic Liver Diseases: Cholesterol Metabolism and Beyond
Abstract
Chronic liver diseases are commonly associated with dysregulated cholesterol metabolism. Proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 (PCSK9) is a serine protease of the proprotein convertase family that is mainly synthetized and secreted by the liver, and represents one of the key regulators of circulating low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol levels. Its ability to bind and induce LDL-receptor degradation, in particular in the liver, increases circulating LDL-cholesterol levels in the blood. Hence, inhibition of PCSK9 has become a very potent tool for the treatment of hypercholesterolemia. Besides PCSK9 limiting entry of LDL-derived cholesterol, affecting multiple cholesterol-related functions in cells, more recent studies have associated PCSK9 with various other cellular processes, including inflammation, fatty acid metabolism, cancerogenesis and visceral adiposity. It is increasingly becoming evident that additional roles for PCSK9 beyond cholesterol homeostasis are crucial for liver physiology in health and disease, often contributing to pathophysiology. This review will summarize studies analyzing circulating and hepatic PCSK9 levels in patients with chronic liver diseases. The factors affecting PCSK9 levels in the circulation and in hepatocytes, clinically relevant studies and the pathophysiological role of PCSK9 in chronic liver injury are discussed.
Keywords: LDL-receptor; NAFLD; PCSK9; alcoholic liver disease; hepatitis C; visceral obesity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

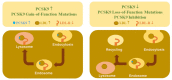


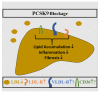
References
-
- Benjannet S., Rhainds D., Essalmani R., Mayne J., Wickham L., Jin W., Asselin M.C., Hamelin J., Varret M., Allard D., et al. NARC-1/PCSK9 and its natural mutants: Zymogen cleavage and effects on the low density lipoprotein (LDL) receptor and LDL cholesterol. J. Biol. Chem. 2004;279:48865–48875. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M409699200. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Cunningham D., Danley D.E., Geoghegan K.F., Griffor M.C., Hawkins J.L., Subashi T.A., Varghese A.H., Ammirati M.J., Culp J.S., Hoth L.R., et al. Structural and biophysical studies of PCSK9 and its mutants linked to familial hypercholesterolemia. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2007;14:413–419. doi: 10.1038/nsmb1235. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

