Protein-Mediated Transformations of Superparamagnetic Nanoparticles Evidenced by Single-Particle Inductively Coupled Plasma Tandem Mass Spectrometry: A Disaggregation Phenomenon
- PMID: 35163012
- PMCID: PMC8835430
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23031088
Protein-Mediated Transformations of Superparamagnetic Nanoparticles Evidenced by Single-Particle Inductively Coupled Plasma Tandem Mass Spectrometry: A Disaggregation Phenomenon
Abstract
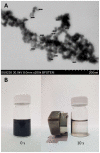
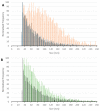
Progress toward translating superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (SPIONs) with specific diagnostic and therapeutic properties for clinical applications depends on developing and implementing appropriate methodologies that would allow in-depth characterizations of their behavior in a real biological environment. Herein, we report a versatile approach for studying interactions between SPIONs and proteins using single-particle inductively coupled plasma tandem mass spectrometry. By monitoring the changes in the size distribution upon exposure to human serum, the formation of stable protein corona is revealed, accompanied by particle disaggregation.
Keywords: human serum; single-particle inductively coupled plasma tandem mass spectrometry; superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Alshehri S., Imam S.S., Rizwanullah M., Akhter S., Mahdi W., Kazi M., Ahmad J. Progress of Cancer Nanotechnology as Diagnostics, Therapeutics, and Theranostics Nanomedicine: Preclinical Promise and Translational Challenges. Pharmaceutics. 2021;13:24. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics13010024. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

