Current and New Challenges in the Management of Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumors: The Role of miRNA-Based Approaches as New Reliable Biomarkers
- PMID: 35163032
- PMCID: PMC8834851
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23031109
Current and New Challenges in the Management of Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumors: The Role of miRNA-Based Approaches as New Reliable Biomarkers
Abstract
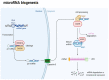
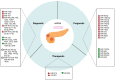
Pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors (PanNETs) are rare tumors; however, their incidence greatly increases with age, and they occur more frequently among the elderly. They represent 5% of all pancreatic tumors, and despite the fact that low-grade tumors often have an indolent evolution, they portend a poor prognosis in an advanced stages and undifferentiated tumors. Additionally, functional pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors greatly impact quality of life due to the various clinical syndromes that result from abnormal hormonal secretion. With limited therapeutic and diagnostic options, patient stratification and selection of optimal therapeutic strategies should be the main focus. Modest improvements in the management of pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors have been achieved in the last years. Therefore, it is imperative to find new biomarkers and therapeutic strategies to improve patient survival and quality of life, limiting the disease burden. MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are small endogenous molecules that modulate the expression of thousands of genes and control numerous critical processes involved in tumor development and progression. New data also suggest the implication of miRNAs in treatment resistance and their potential as prognostic or diagnostic biomarkers and therapeutic targets. In this review, we discusses the current and new challenges in the management of PanNETs, including genetic and epigenetic approaches. Furthermore, we summarize the available data on miRNAs as potential prognostic, predictive, or diagnostic biomarkers and discuss their function as future therapeutic targets.
Keywords: MicroRNAs; biomarkers; diagnosis; genetic; pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors (PanNETs); prognosis; therapeutic.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
miRNA profile in pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors: Preliminary results.Sci Prog. 2025 Jan-Mar;108(1):368504251326864. doi: 10.1177/00368504251326864. Epub 2025 Mar 28. Sci Prog. 2025. PMID: 40152231 Free PMC article.
-
Pancreatic neuroendocrine neoplasms (pNENs): Genetic and environmental biomarkers for risk of occurrence and prognosis.Semin Cancer Biol. 2025 Jul;112:112-125. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2025.03.005. Epub 2025 Mar 28. Semin Cancer Biol. 2025. PMID: 40158764 Review.
-
Genetics of pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors: implications for the clinic.Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2015;9(11):1407-19. doi: 10.1586/17474124.2015.1092383. Epub 2015 Sep 28. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2015. PMID: 26413978 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Molecular and Clinical Landscape of Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumors.Pancreas. 2019 Jan;48(1):9-21. doi: 10.1097/MPA.0000000000001189. Pancreas. 2019. PMID: 30531241 Review.
-
Clinical application of microRNA testing in neuroendocrine tumors of the gastrointestinal tract.Molecules. 2014 Feb 21;19(2):2458-68. doi: 10.3390/molecules19022458. Molecules. 2014. PMID: 24566314 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Exploring the theranostic potentials of miRNA and epigenetic networks in autoimmune diseases: A comprehensive review.Immun Inflamm Dis. 2023 Dec;11(12):e1121. doi: 10.1002/iid3.1121. Immun Inflamm Dis. 2023. PMID: 38156400 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Circulating microRNAs as Potential Biomarkers in Pancreatic Cancer-Advances and Challenges.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Aug 28;24(17):13340. doi: 10.3390/ijms241713340. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37686149 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evaluation of a blood miRNA/mRNA signature to follow-up Lu-PRRT therapy for G1/G2 intestinal neuroendocrine tumors.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024 Jun 14;15:1385079. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1385079. eCollection 2024. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 38948517 Free PMC article.
-
Biochemical Markers for Neuroendocrine Tumors: Traditional Circulating Markers and Recent Development-A Comprehensive Review.Diagnostics (Basel). 2024 Jun 18;14(12):1289. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics14121289. Diagnostics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38928704 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epigenetic Regulation in Gastroenteropancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumors.Front Oncol. 2022 Jun 7;12:901435. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.901435. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35747820 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Choe J., Kim K.W., Kim H.J., Kim D.W., Kim K.P., Hong S.-M., Ryu J.-S., Tirumani S.H., Krajewski K., Ramaiya N. What Is New in the 2017 World Health Organization Classification and 8th American Joint Committee on Cancer Staging System for Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Neoplasms? Korean J. Radiol. 2019;20:5. doi: 10.3348/kjr.2018.0040. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lesén E., Granfeldt D., Houchard A., Berthon A., Dinet J., Gabriel S., Björstad Å., Björholt I., Elf A.K., Johanson V. Cost-of-illness of metastatic gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine tumours in Sweden—A population-based register-linkage study. Eur. J. Cancer Care. 2019;28:e12983. doi: 10.1111/ecc.12983. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical