Challenging Approach to the Development of Novel Estrogen Receptor Modulators Based on the Chemical Properties of Guaiazulene
- PMID: 35163039
- PMCID: PMC8835499
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23031113
Challenging Approach to the Development of Novel Estrogen Receptor Modulators Based on the Chemical Properties of Guaiazulene
Abstract
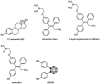
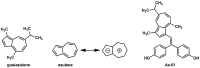
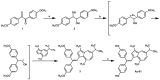
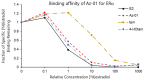
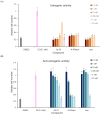
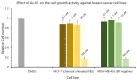
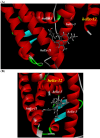
Tamoxifen, a therapeutic agent for breast cancer, has been associated with genetic polymorphisms in the metabolism of N,N-dialkylaminoethyl substituent, which plays an important role in the expression of selective estrogen receptor modulator (SERM) activity. To solve this problem, we developed a novel estrogen receptor (ER) modulator, Az-01, on the basis of the aromaticity, dipole moment, and isopropyl group of guaiazulene. Az-01 showed four-fold lower binding affinity for ER than E2 but had similar ER-binding affinity to that of 4-hydroxytamoxifen (4-HOtam). Unlike tamoxifen, Az-01 acted as a partial agonist with very weak estrogenic activity at high concentrations when used alone, and it showed potent anti-estrogenic activity in the presence of E2. The cell proliferation and inhibition activities of Az-01 were specific to ER-expressing MCF-7 cells, and no effect of Az-01 on other cell proliferation signals was observed. These findings are important for the development of new types of SERMs without the N,N-dialkylaminoethyl substituent as a privileged functional group for SERMs.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

