Production and Biochemical Characterization of Dimeric Recombinant Gremlin-1
- PMID: 35163075
- PMCID: PMC8835488
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23031151
Production and Biochemical Characterization of Dimeric Recombinant Gremlin-1
Abstract
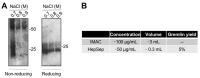
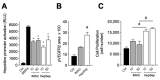
Gremlin-1 is a secreted cystine-knot protein that acts as an antagonist of bone morphogenetic proteins (BMPs), and as a ligand of heparin and the vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 (VEGFR2), thus regulating several physiological and pathological processes, including embryonic development, tissue fibrosis and cancer. Gremlin-1 exerts all these biological activities only in its homodimeric form. Here, we propose a multi-step approach for the expression and purification of homodimeric, fully active, histidine-tagged recombinant gremlin-1, using mammalian HEK293T cells. Ion metal affinity chromatography (IMAC) of crude supernatant followed by heparin-affinity chromatography enables obtaining a highly pure recombinant dimeric gremlin-1 protein, exhibiting both BMP antagonist and potent VEGFR2 agonist activities.
Keywords: HEK293T expression system; cystine-knot protein; dimer; gremlin-1.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The binding of the bone morphogenetic protein antagonist gremlin to kidney heparan sulfate: Such binding is not essential for BMP antagonism.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2017 Feb;83:39-46. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2016.12.006. Epub 2016 Dec 12. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2017. PMID: 27979781
-
Monomeric gremlin is a novel vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2 antagonist.Oncotarget. 2016 Jun 7;7(23):35353-68. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.9286. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27174917 Free PMC article.
-
Gremlin is a novel agonist of the major proangiogenic receptor VEGFR2.Blood. 2010 Nov 4;116(18):3677-80. doi: 10.1182/blood-2010-06-291930. Epub 2010 Jul 21. Blood. 2010. PMID: 20660291
-
Molecular Regulation of Notch Signaling by Gremlin.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020;1227:81-94. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-36422-9_6. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020. PMID: 32072500 Review.
-
BMP signalling: agony and antagony in the family.Trends Cell Biol. 2015 May;25(5):249-64. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2014.12.004. Epub 2015 Jan 12. Trends Cell Biol. 2015. PMID: 25592806 Review.
Cited by
-
Pan-cancer multi-omics analysis to identify the potential pro-oncogenic properties of GREM1 as a promising targets for cancer prognosis and therapeutics.Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 2025 Jan-Dec;39:3946320251331850. doi: 10.1177/03946320251331850. Epub 2025 Apr 15. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40231657 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanobiology of the relocation of proteins in advecting cells: in vitro experiments, multi-physics modeling, and simulations.Biomech Model Mechanobiol. 2023 Aug;22(4):1267-1287. doi: 10.1007/s10237-023-01717-2. Epub 2023 Apr 17. Biomech Model Mechanobiol. 2023. PMID: 37067608 Free PMC article.
-
Gremlin1: a BMP antagonist with therapeutic potential in Oncology.Invest New Drugs. 2024 Dec;42(6):716-727. doi: 10.1007/s10637-024-01474-8. Epub 2024 Sep 30. Invest New Drugs. 2024. PMID: 39347850 Review.
-
Ex.50.T aptamer impairs tumor-stroma cross-talk in breast cancer by targeting gremlin-1.Cell Death Discov. 2025 Mar 11;11(1):94. doi: 10.1038/s41420-025-02363-6. Cell Death Discov. 2025. PMID: 40069570 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

