Cancer as a Metabolic Disorder
- PMID: 35163079
- PMCID: PMC8835572
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23031155
Cancer as a Metabolic Disorder
Abstract
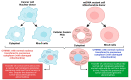
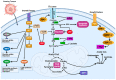
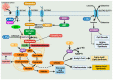
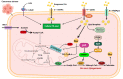
Cancer has long been considered a genetic disease characterized by a myriad of mutations that drive cancer progression. Recent accumulating evidence indicates that the dysregulated metabolism in cancer cells is more than a hallmark of cancer but may be the underlying cause of the tumor. Most of the well-characterized oncogenes or tumor suppressor genes function to sustain the altered metabolic state in cancer. Here, we review evidence supporting the altered metabolic state in cancer including key alterations in glucose, glutamine, and fatty acid metabolism. Unlike genetic alterations that do not occur in all cancer types, metabolic alterations are more common among cancer subtypes and across cancers. Recognizing cancer as a metabolic disorder could unravel key diagnostic and treatments markers that can impact approaches used in cancer management.
Keywords: cancer; fatty acids; glucose; glutamine; metabolism.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

