Comprehensive Profiling of Paper Mulberry (Broussonetia papyrifera) Crotonylome Reveals the Significance of Lysine Crotonylation in Young Leaves
- PMID: 35163093
- PMCID: PMC8834973
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23031173
Comprehensive Profiling of Paper Mulberry (Broussonetia papyrifera) Crotonylome Reveals the Significance of Lysine Crotonylation in Young Leaves
Abstract
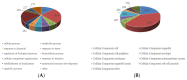
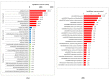
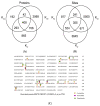
Lysine crotonylation is a newly discovered and reversible posttranslational modification involved in various biological processes, especially metabolism regulation. A total of 5159 lysine crotonylation sites in 2272 protein groups were identified. Twenty-seven motifs were found to be the preferred amino acid sequences for crotonylation sites. Functional annotation analyses revealed that most crotonylated proteins play important roles in metabolic processes and photosynthesis. Bioinformatics analysis suggested that lysine crotonylation preferentially targets a variety of important biological processes, including ribosome, glyoxylate and dicarboxylate metabolism, carbon fixation in photosynthetic organisms, proteasome and the TCA cycle, indicating lysine crotonylation is involved in the common mechanism of metabolic regulation. A protein interaction network analysis revealed that diverse interactions are modulated by protein crotonylation. These results suggest that lysine crotonylation is involved in a variety of biological processes. HSP70 is a crucial protein involved in protecting plant cells and tissues from thermal or abiotic stress responses, and HSP70 protein was found to be crotonylated in paper mulberry. This systematic analysis provides the first comprehensive analysis of lysine crotonylation in paper mulberry and provides important resources for further study on the regulatory mechanism and function of the lysine crotonylated proteome.
Keywords: PPI; lysine crotonylation; paper mulberry; plant metabolism; posttranslational modification.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest with the contents of this article.
Figures








Similar articles
-
Ammonium triggered the response mechanism of lysine crotonylome in tea plants.BMC Genomics. 2019 May 6;20(1):340. doi: 10.1186/s12864-019-5716-z. BMC Genomics. 2019. PMID: 31060518 Free PMC article.
-
Global Involvement of Lysine Crotonylation in Protein Modification and Transcription Regulation in Rice.Mol Cell Proteomics. 2018 Oct;17(10):1922-1936. doi: 10.1074/mcp.RA118.000640. Epub 2018 Jul 18. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2018. PMID: 30021883 Free PMC article.
-
First comprehensive proteome analysis of lysine crotonylation in seedling leaves of Nicotiana tabacum.Sci Rep. 2017 Jun 7;7(1):3013. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-03369-6. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28592803 Free PMC article.
-
Functions and mechanisms of lysine crotonylation.J Cell Mol Med. 2019 Nov;23(11):7163-7169. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.14650. Epub 2019 Sep 1. J Cell Mol Med. 2019. PMID: 31475443 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Function and mechanism of lysine crotonylation in health and disease.QJM. 2024 Oct 1;117(10):695-708. doi: 10.1093/qjmed/hcae034. QJM. 2024. PMID: 38390964 Review.
Cited by
-
The crotonylated and succinylated proteins of jujube involved in phytoplasma-stress responses.BMC Biol. 2024 May 15;22(1):113. doi: 10.1186/s12915-024-01917-x. BMC Biol. 2024. PMID: 38750524 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Christopher T., Tsodikova S., Gregory J. Protein Posttranslational Modifications: The Chemistry of Proteome Diversifications. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2005;44:7342–7372. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

