Oleacein Attenuates Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Inflammation in THP-1-Derived Macrophages by the Inhibition of TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB Pathway
- PMID: 35163130
- PMCID: PMC8835840
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23031206
Oleacein Attenuates Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Inflammation in THP-1-Derived Macrophages by the Inhibition of TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB Pathway
Abstract
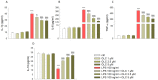
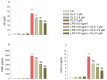
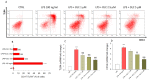
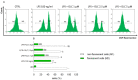
It is known that plant phenolic compounds exert anti-inflammatory activity through both anti-oxidant effects and modulation of pivotal pro-inflammatory factors. Recently, Olea europaea has been studied as a natural source of bioactive molecules; however, few studies have focused on the biological effect of oleacein (OLC), the most abundant secoiridoid. Therefore, the aim of this study was to investigate the potential anti-oxidant activity of OLC, as well as to study its anti-inflammatory effect in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated THP-1-derived macrophages. LPS brought a dramatic increase of both release and gene expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines (IL-6, IL-1β and TNF-α), as well as a decrease of anti-inflammatory ones (IL-10), the effects of which are reverted by OLC. Moreover, it reduced the levels of COX-2, NO and PGE2 elicited by LPS exposure in THP-1 macrophages. Interestingly, OLC modulated inflammatory signaling pathways through the inhibition of CD14/TLR4/CD14/MyD88 axis and the activation of NF-κB. Finally, OLC showed relevant anti-oxidant capability, assessed by abiotic assays, and reduced the intracellular amount of ROS generated by LPS exposure in THP-1 macrophages. Overall, these results suggest that the anti-oxidant activity and anti-inflammatory effect of OLC may cooperate in its protective effect against inflammatory stressors, thus being a possible alternative pharmacological strategy aimed at reducing the inflammatory process.
Keywords: CD14; LPS; MyD88; NF-κB; Olea europea; ROS; THP-1 monocytes; TLR4; inflammation; oleacein.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Adenosine 5'-Trisphosphate in Lipopolysaccharide-Stimulated Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells Through Negative Regulation of Toll-Like Receptor MyD88 Signaling.DNA Cell Biol. 2019 Dec;38(12):1557-1563. doi: 10.1089/dna.2019.4773. Epub 2019 Oct 3. DNA Cell Biol. 2019. PMID: 31580158
-
Melatonin modulates TLR4-mediated inflammatory genes through MyD88- and TRIF-dependent signaling pathways in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated RAW264.7 cells.J Pineal Res. 2012 Nov;53(4):325-34. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-079X.2012.01002.x. Epub 2012 Apr 27. J Pineal Res. 2012. PMID: 22537289
-
Anti-inflammation Effects of Sinomenine on Macrophages through Suppressing Activated TLR4/NF-κB Signaling Pathway.Curr Med Sci. 2020 Feb;40(1):130-137. doi: 10.1007/s11596-020-2156-6. Epub 2020 Mar 13. Curr Med Sci. 2020. PMID: 32166675
-
Diethyl Blechnic Exhibits Anti-Inflammatory and Antioxidative Activity via the TLR4/MyD88 Signaling Pathway in LPS-Stimulated RAW264.7 Cells.Molecules. 2019 Dec 9;24(24):4502. doi: 10.3390/molecules24244502. Molecules. 2019. PMID: 31835323 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Tanshinone IIA in LPS-Stimulated RAW264.7 Macrophages via miRNAs and TLR4-NF-κB Pathway.Inflammation. 2016 Feb;39(1):375-384. doi: 10.1007/s10753-015-0259-1. Inflammation. 2016. PMID: 26639663
Cited by
-
Effects of Dietary Oleacein Treatment on Endothelial Dysfunction and Lupus Nephritis in Balb/C Pristane-Induced Mice.Antioxidants (Basel). 2023 Jun 19;12(6):1303. doi: 10.3390/antiox12061303. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37372034 Free PMC article.
-
The Inhibition of Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinases (MAPKs) and NF-κB Underlies the Neuroprotective Capacity of a Cinnamon/Curcumin/Turmeric Spice Blend in Aβ-Exposed THP-1 Cells.Molecules. 2023 Dec 5;28(24):7949. doi: 10.3390/molecules28247949. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 38138438 Free PMC article.
-
Oleuropein mediated autophagy begets antimalarial drug resistance.Front Microbiol. 2024 Aug 20;15:1453998. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1453998. eCollection 2024. Front Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39228384 Free PMC article.
-
Sirtuins as Players in the Signal Transduction of Citrus Flavonoids.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Feb 6;25(4):1956. doi: 10.3390/ijms25041956. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38396635 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The potential effect of natural antioxidants on endothelial dysfunction associated with arterial hypertension.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2024 Feb 2;11:1345218. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2024.1345218. eCollection 2024. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2024. PMID: 38370153 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Maugeri A., Cirmi S., Minciullo P.L., Gangemi S., Calapai G., Mollace V., Navarra M. Citrus fruits and inflammaging: A systematic review. Phytochem. Rev. 2019;18:1025–1049. doi: 10.1007/s11101-019-09613-3. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

