The Pathomechanism, Antioxidant Biomarkers, and Treatment of Oxidative Stress-Related Eye Diseases
- PMID: 35163178
- PMCID: PMC8835903
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23031255
The Pathomechanism, Antioxidant Biomarkers, and Treatment of Oxidative Stress-Related Eye Diseases
Abstract
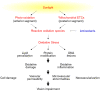
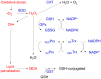
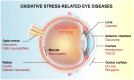
Oxidative stress is an important pathomechanism found in numerous ocular degenerative diseases. To provide a better understanding of the mechanism and treatment of oxidant/antioxidant imbalance-induced ocular diseases, this article summarizes and provides updates on the relevant research. We review the oxidative damage (e.g., lipid peroxidation, DNA lesions, autophagy, and apoptosis) that occurs in different areas of the eye (e.g., cornea, anterior chamber, lens, retina, and optic nerve). We then introduce the antioxidant mechanisms present in the eye, as well as the ocular diseases that occur as a result of antioxidant imbalances (e.g., keratoconus, cataracts, age-related macular degeneration, and glaucoma), the relevant antioxidant biomarkers, and the potential of predictive diagnostics. Finally, we discuss natural antioxidant therapies for oxidative stress-related ocular diseases.
Keywords: antioxidant biomarkers; antioxidant therapy; ocular diseases; oxidative stress.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Nita M., Grzybowski A. The Role of the Reactive Oxygen Species and Oxidative Stress in the Pathomechanism of the Age-Related Ocular Diseases and Other Pathologies of the Anterior and Posterior Eye Segments in Adults. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2016;2016:3164734. doi: 10.1155/2016/3164734. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

