Floating Ricobendazole Delivery Systems: A 3D Printing Method by Co-Extrusion of Sodium Alginate and Calcium Chloride
- PMID: 35163203
- PMCID: PMC8835811
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23031280
Floating Ricobendazole Delivery Systems: A 3D Printing Method by Co-Extrusion of Sodium Alginate and Calcium Chloride
Abstract
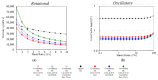
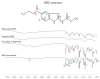
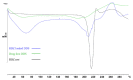
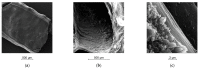
At present, the use of benzimidazole drugs in veterinary medicine is strongly limited by both pharmacokinetics and formulative issues. In this research, the possibility of applying an innovative semi-solid extrusion 3D printing process in a co-axial configuration was speculated, with the aim of producing a new gastro-retentive dosage form loaded with ricobendazole. To obtain the drug delivery system (DDS), the ionotropic gelation of alginate in combination with a divalent cation during the extrusion was exploited. Two feeds were optimized in accordance with the printing requirements and the drug chemical properties: the crosslinking ink, i.e., a water ethanol mixture containing CaCl2 at two different ratios 0.05 M and 0.1 M, hydroxyethyl cellulose 2% w/v, Tween 85 0.1% v/v and Ricobendazole 5% w/v; and alginate ink, i.e., a sodium alginate solution at 6% w/v. The characterization of the dried DDS obtained from the extrusion of gels containing different amounts of calcium chloride showed a limited effect on the ink extrudability of the crosslinking agent, which on the contrary strongly influenced the final properties of the DDS, with a difference in the polymeric matrix toughness and resulting effects on floating time and drug release.
Keywords: alginate ionotropic gelation; floating DDS; semi-solid extrusion 3D printing.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

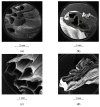
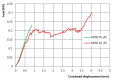
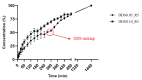
References
-
- Spasov A., Smirnova L., Iezhitsa I., Sergeeva S., Ozerov A. Pharmacokinetics of benzimidazole derivatives. Vopr. Meditsinskoi Khimii. 2002;48:233–258. - PubMed
-
- Lopez-Garcia M.L., Torrado-Duran S., Torrado-Duran J., Martínez-Fernández A.R., Bolás-Fernández F. Albendazole versus ricobendazole (albendazole-sulphoxide) against enteral and parenteral stages of Trichinella spiralis in mice. Int. J. Parasitol. 1997;27:781–785. doi: 10.1016/S0020-7519(97)00052-0. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

