Cell Cycle-Dependent Transcription: The Cyclin Dependent Kinase Cdk1 Is a Direct Regulator of Basal Transcription Machineries
- PMID: 35163213
- PMCID: PMC8835803
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23031293
Cell Cycle-Dependent Transcription: The Cyclin Dependent Kinase Cdk1 Is a Direct Regulator of Basal Transcription Machineries
Abstract
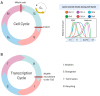
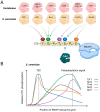
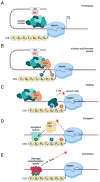
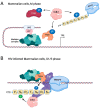
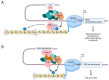
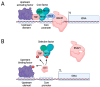
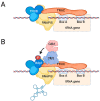
The cyclin-dependent kinase Cdk1 is best known for its function as master regulator of the cell cycle. It phosphorylates several key proteins to control progression through the different phases of the cell cycle. However, studies conducted several decades ago with mammalian cells revealed that Cdk1 also directly regulates the basal transcription machinery, most notably RNA polymerase II. More recent studies in the budding yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae have revisited this function of Cdk1 and also revealed that Cdk1 directly controls RNA polymerase III activity. These studies have also provided novel insight into the physiological relevance of this process. For instance, cell cycle-stage-dependent activity of these complexes may be important for meeting the increased demand for various proteins involved in housekeeping, metabolism, and protein synthesis. Recent work also indicates that direct regulation of the RNA polymerase II machinery promotes cell cycle entry. Here, we provide an overview of the regulation of basal transcription by Cdk1, and we hypothesize that the original function of the primordial cell-cycle CDK was to regulate RNAPII and that it later evolved into specialized kinases that govern various aspects of the transcription machinery and the cell cycle.
Keywords: Cdk1; RNA polymerase; cell cycle; cyclin-dependent kinase; transcription.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

