Exosomal miRNAs from Prostate Cancer Impair Osteoblast Function in Mice
- PMID: 35163219
- PMCID: PMC8836054
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23031285
Exosomal miRNAs from Prostate Cancer Impair Osteoblast Function in Mice
Abstract
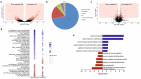
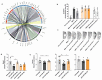
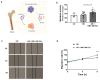
Prostate cancer (PCa) is the most frequent malignancy in older men with a high propensity for bone metastases. Characteristically, PCa causes osteosclerotic lesions as a result of disrupted bone remodeling. Extracellular vesicles (EVs) participate in PCa progression by conditioning the pre-metastatic niche. However, how EVs mediate the cross-talk between PCa cells and osteoprogenitors in the bone microenvironment remains poorly understood. We found that EVs derived from murine PCa cell line RM1-BM increased metabolic activity, vitality, and cell proliferation of osteoblast precursors by >60%, while significantly impairing mineral deposition (-37%). The latter was further confirmed in two complementary in vivo models of ossification. Accordingly, gene and protein set enrichments of osteoprogenitors exposed to EVs displayed significant downregulation of osteogenic markers and upregulation of proinflammatory factors. Additionally, transcriptomic profiling of PCa-EVs revealed the abundance of three microRNAs, miR-26a-5p, miR-27a-3p, and miR-30e-5p involved in the suppression of BMP-2-induced osteogenesis in vivo, suggesting the critical role of these EV-derived miRNAs in PCa-mediated suppression of osteoblast activity. Taken together, our results indicate the importance of EV cargo in cancer-bone cross-talk in vitro and in vivo and suggest that exosomal miRNAs may contribute to the onset of osteosclerotic bone lesions in PCa.
Keywords: bone metastases; extracellular vesicles; miRNA; osteoprogenitors; prostate cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare the following financial interest/personal relationships which may be considered as potential competing interest: A.M.d.J.D. is employed by Dewpoint Therapeutics; M.H. is co-founder and share-holder of TAmiRNA GmbH (Vienna, Austria). All the other authors have no competing financial interest or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Osteoblast-derived exosomal miR-140-3p targets ACER2 and increases the progression of prostate cancer via the AKT/mTOR pathway-mediated inhibition of autophagy.FASEB J. 2024 Dec 15;38(23):e70206. doi: 10.1096/fj.202401480R. FASEB J. 2024. PMID: 39625343
-
MicroRNA-183-5p Increases with Age in Bone-Derived Extracellular Vesicles, Suppresses Bone Marrow Stromal (Stem) Cell Proliferation, and Induces Stem Cell Senescence.Tissue Eng Part A. 2017 Nov;23(21-22):1231-1240. doi: 10.1089/ten.TEA.2016.0525. Epub 2017 Apr 28. Tissue Eng Part A. 2017. PMID: 28363268 Free PMC article.
-
Prostate cancer extracellular vesicles mediate intercellular communication with bone marrow cells and promote metastasis in a cholesterol-dependent manner.J Extracell Vesicles. 2020 Dec;10(2):e12042. doi: 10.1002/jev2.12042. Epub 2020 Dec 31. J Extracell Vesicles. 2020. PMID: 33408816 Free PMC article.
-
Communication of prostate cancer cells with bone cells via extracellular vesicle RNA; a potential mechanism of metastasis.Oncogene. 2019 Mar;38(10):1751-1763. doi: 10.1038/s41388-018-0540-5. Epub 2018 Oct 23. Oncogene. 2019. PMID: 30353168 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Systematic Analysis of Tissue-Derived and Biofluid Extracellular Vesicle miRNAs Associated with Prostate Cancer.Adv Biol (Weinh). 2023 Jul;7(7):e2200327. doi: 10.1002/adbi.202200327. Epub 2023 Jun 9. Adv Biol (Weinh). 2023. PMID: 37300338
Cited by
-
Signaling-induced systematic repression of miRNAs uncovers cancer vulnerabilities and targeted therapy sensitivity.Cell Rep Med. 2023 Oct 17;4(10):101200. doi: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2023.101200. Epub 2023 Sep 20. Cell Rep Med. 2023. PMID: 37734378 Free PMC article.
-
Current landscape of exosomal non-coding RNAs in prostate cancer: Modulators and biomarkers.Noncoding RNA Res. 2024 Jul 20;9(4):1351-1362. doi: 10.1016/j.ncrna.2024.07.003. eCollection 2024 Dec. Noncoding RNA Res. 2024. PMID: 39247145 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role and mechanisms of exosome microRNA in regulating metastasis within the tumor microenvironment of prostate cancer.Front Oncol. 2025 Jun 10;15:1580314. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1580314. eCollection 2025. Front Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40556678 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biomarkers for Prostate Cancer Bone Metastasis Detection and Prediction.J Pers Med. 2023 Apr 22;13(5):705. doi: 10.3390/jpm13050705. J Pers Med. 2023. PMID: 37240875 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Delineating the role of extracellular vesicles in cancer metastasis: A comprehensive review.Front Immunol. 2022 Aug 19;13:966661. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.966661. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36059497 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Koo K.C., Park S.U., Kim K.H., Rha K.H., Hong S.J., Yang S.C., Chung B.H. Prognostic Impacts of Metastatic Site and Pain on Progression to Castrate Resistance and Mortality in Patients with Metastatic Prostate Cancer. Yonsei Med. J. 2015;56:1206–1212. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2015.56.5.1206. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

