Wnt and PI3K/Akt/mTOR Survival Pathways as Therapeutic Targets in Glioblastoma
- PMID: 35163279
- PMCID: PMC8836096
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23031353
Wnt and PI3K/Akt/mTOR Survival Pathways as Therapeutic Targets in Glioblastoma
Abstract
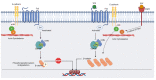
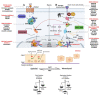
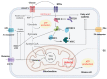
Glioblastoma (GBM) is a devastating type of brain tumor, and current therapeutic treatments, including surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation, are palliative at best. The design of effective and targeted chemotherapeutic strategies for the treatment of GBM require a thorough analysis of specific signaling pathways to identify those serving as drivers of GBM progression and invasion. The Wnt/β-catenin and PI3K/Akt/mTOR (PAM) signaling pathways are key regulators of important biological functions that include cell proliferation, epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), metabolism, and angiogenesis. Targeting specific regulatory components of the Wnt/β-catenin and PAM pathways has the potential to disrupt critical brain tumor cell functions to achieve critical advancements in alternative GBM treatment strategies to enhance the survival rate of GBM patients. In this review, we emphasize the importance of the Wnt/β-catenin and PAM pathways for GBM invasion into brain tissue and explore their potential as therapeutic targets.
Keywords: GBM survival; PI3K/Akt/mTOR; Wnt/β-catenin; autophagy; glioblastoma.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Hombach-Klonisch S., Mehrpour M., Shojaei S., Harlos C., Pitz M., Hamai A., Siemianowicz K., Likus W., Wiechec E., Toyota B.D., et al. Glioblastoma and chemoresistance to alkylating agents: Involvement of apoptosis, autophagy, and unfolded protein response. Pharmacol. Ther. 2018;184:13–41. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2017.10.017. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Shojaei S., Koleini N., Samiei E., Aghaei M., Cole L.K., Alizadeh J., Islam I., Vosoughi A., Albokashy M., Butterfield Y., et al. Simvastatin increases temozolomide-induced cell death by targeting the fusion of autophagosomes and lysosomes. FEBS J. 2020;287:1005–1034. doi: 10.1111/febs.15069. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Siebzehnrubl F.A., Silver D.J., Tugertimur B., Deleyrolle L.P., Siebzehnrubl D., Sarkisian M.R., Devers K.G., Yachnis A.T., Kupper M.D., Neal D., et al. The ZEB1 pathway links glioblastoma initiation, invasion and chemoresistance. EMBO Mol. Med. 2013;5:1196–1212. doi: 10.1002/emmm.201302827. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

