Signaling Mechanisms and Pharmacological Modulators Governing Diverse Aquaporin Functions in Human Health and Disease
- PMID: 35163313
- PMCID: PMC8836214
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23031388
Signaling Mechanisms and Pharmacological Modulators Governing Diverse Aquaporin Functions in Human Health and Disease
Abstract
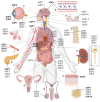
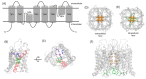
The aquaporins (AQPs) are a family of small integral membrane proteins that facilitate the bidirectional transport of water across biological membranes in response to osmotic pressure gradients as well as enable the transmembrane diffusion of small neutral solutes (such as urea, glycerol, and hydrogen peroxide) and ions. AQPs are expressed throughout the human body. Here, we review their key roles in fluid homeostasis, glandular secretions, signal transduction and sensation, barrier function, immunity and inflammation, cell migration, and angiogenesis. Evidence from a wide variety of studies now supports a view of the functions of AQPs being much more complex than simply mediating the passive flow of water across biological membranes. The discovery and development of small-molecule AQP inhibitors for research use and therapeutic development will lead to new insights into the basic biology of and novel treatments for the wide range of AQP-associated disorders.
Keywords: aquaporin (AQP); facilitated diffusion; fluid; membranes; osmosis; secretion; signaling; water.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors confirm there are no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Molecular mechanisms governing aquaporin relocalisation.Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr. 2022 Apr 1;1864(4):183853. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2021.183853. Epub 2021 Dec 30. Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr. 2022. PMID: 34973181 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Aquaporins in sepsis- an update.Front Immunol. 2024 Oct 31;15:1495206. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1495206. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39544938 Free PMC article. Review.
-
More than just water channels: unexpected cellular roles of aquaporins.J Cell Sci. 2005 Aug 1;118(Pt 15):3225-32. doi: 10.1242/jcs.02519. J Cell Sci. 2005. PMID: 16079275 Review.
-
Urea transport mediated by aquaporin water channel proteins.Subcell Biochem. 2014;73:227-65. doi: 10.1007/978-94-017-9343-8_14. Subcell Biochem. 2014. PMID: 25298348
-
Aquaporins: important but elusive drug targets.Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2014 Apr;13(4):259-77. doi: 10.1038/nrd4226. Epub 2014 Mar 14. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2014. PMID: 24625825 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Aquaporins: Gatekeepers of Fluid Dynamics in Traumatic Brain Injury.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jun 14;25(12):6553. doi: 10.3390/ijms25126553. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38928258 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Novel Rodent Model of Hypertensive Cerebral Small Vessel Disease with White Matter Hyperintensities and Peripheral Oxidative Stress.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 May 25;23(11):5915. doi: 10.3390/ijms23115915. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35682594 Free PMC article.
-
Aquaporins alteration revealed kidney damages in cerebral ischemia/reperfusion rats.Heliyon. 2024 May 18;10(10):e31532. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e31532. eCollection 2024 May 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38807874 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of vitamin D3 and a stinging nettle extract on the gastric tissue of rats administered with trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid.Vet Med (Praha). 2024 Mar 28;69(3):84-93. doi: 10.17221/111/2023-VETMED. eCollection 2024 Mar. Vet Med (Praha). 2024. PMID: 38623153 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of Soluble Guanylate Cyclase on Cardiac, Vascular, and Renal Structure and Function: A Physiopathological Insight.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 May 9;26(10):4550. doi: 10.3390/ijms26104550. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40429695 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Benga G., Popescu O., Borza V., Pop V.I., Muresan A., Mocsy I., Brain A., Wrigglesworth J.M. Water permeability in human erythrocytes: Identification of membrane proteins involved in water transport. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 1986;41:252–262. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- MR/N029453/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- G-1003/PUK_/Parkinson's UK/United Kingdom
- MR/P007058/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- H-1102/PUK_/Parkinson's UK/United Kingdom
- H-1301/PUK_/Parkinson's UK/United Kingdom
- J-0901/PUK_/Parkinson's UK/United Kingdom
- MC_EX_MR/N50192X/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MR/L023784/2/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MR/M024962/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- PG/10/54/28460/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- K-1003/PUK_/Parkinson's UK/United Kingdom
- G-0801/PUK_/Parkinson's UK/United Kingdom
- BB/D012910/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

