Metabolites of Cannabis Induce Cardiac Toxicity and Morphological Alterations in Cardiac Myocytes
- PMID: 35163321
- PMCID: PMC8835806
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23031401
Metabolites of Cannabis Induce Cardiac Toxicity and Morphological Alterations in Cardiac Myocytes
Abstract
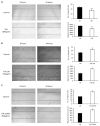
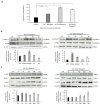
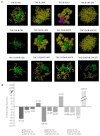
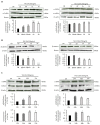
Cannabis is one of the most commonly used recreational drugs worldwide. Rrecent epidemiology studies have linked increased cardiac complications to cannabis use. However, this literature is predominantly based on case incidents and post-mortem investigations. This study elucidates the molecular mechanism of Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), and its primary metabolites 11-Hydroxy-Δ9-THC (THC-OH) and 11-nor-9-carboxy-Δ⁹-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC-COOH). Treatment of cardiac myocytes with THC-OH and THC-COOH increased cell migration and proliferation (p < 0.05), with no effect on cell adhesion, with higher doses (250-100 ng/mL) resulting in increased cell death and significant deterioration in cellular architecture. Conversely, no changes in cell morphology or viability were observed in response to THC. Expression of key ECM proteins α-SMA and collagen were up-regulated in response to THC-OH and THC-COOH treatments with concomitant modulation of PI3K and MAPK signalling. Investigations in the planarian animal model Polycelis nigra demonstrated that treatments with cannabinoid metabolites resulted in increased protein deposition at transection sites while higher doses resulted in significant lethality and decline in regeneration. These results highlight that the key metabolites of cannabis elicit toxic effects independent of the parent and psychoactive compound, with implications for cardiotoxicity relating to hypertrophy and fibrogenesis.
Keywords: THC; cannabis; cardiac myocytes; cardiac toxicity; cytoskeleton; planaria.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Plasma and urine profiles of Delta9-tetrahydrocannabinol and its metabolites 11-hydroxy-Delta9-tetrahydrocannabinol and 11-nor-9-carboxy-Delta9-tetrahydrocannabinol after cannabis smoking by male volunteers to estimate recent consumption by athletes.Anal Bioanal Chem. 2010 Apr;396(7):2493-502. doi: 10.1007/s00216-009-3431-3. Epub 2010 Jan 30. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2010. PMID: 20112012
-
Driving under the influence of cannabis: A 5-year retrospective Italian study.Forensic Sci Int. 2023 Dec;353:111854. doi: 10.1016/j.forsciint.2023.111854. Epub 2023 Oct 15. Forensic Sci Int. 2023. PMID: 37922577
-
Urinary excretion profiles of 11-nor-9-carboxy-delta9-tetrahydrocannabinol and 11-hydroxy-delta9-THC: cannabinoid metabolites to creatinine ratio study IV.Forensic Sci Int. 2004 Jul 16;143(2-3):147-52. doi: 10.1016/j.forsciint.2004.02.034. Forensic Sci Int. 2004. PMID: 15240035
-
The Utility of THC Cutoff Levels in Blood and Saliva for Detection of Impaired Driving.Cannabis Cannabinoid Res. 2023 Jun;8(3):408-413. doi: 10.1089/can.2022.0187. Epub 2023 Feb 2. Cannabis Cannabinoid Res. 2023. PMID: 36730769 Review.
-
The impact of pregnancy and associated hormones on the pharmacokinetics of Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol.Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 2024 Jan-Feb;20(1-2):73-93. doi: 10.1080/17425255.2024.2309213. Epub 2024 Mar 4. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 2024. PMID: 38258511 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Case Report Highlighting Cardiovascular Effects of Concomitant Use of Methamphetamine and Marijuana.Cureus. 2022 Aug 10;14(8):e27866. doi: 10.7759/cureus.27866. eCollection 2022 Aug. Cureus. 2022. PMID: 36110480 Free PMC article.
-
Phytocannabinoids Stimulate Rejuvenation and Prevent Cellular Senescence in Human Dermal Fibroblasts.Cells. 2022 Dec 6;11(23):3939. doi: 10.3390/cells11233939. Cells. 2022. PMID: 36497198 Free PMC article.
-
Why Do Marijuana and Synthetic Cannabimimetics Induce Acute Myocardial Infarction in Healthy Young People?Cells. 2022 Mar 28;11(7):1142. doi: 10.3390/cells11071142. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35406706 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

