Selective Boosting of CCR7-Acting Chemokines; Short Peptides Boost Chemokines with Short Basic Tails, Longer Peptides Boost Chemokines with Long Basic Tails
- PMID: 35163323
- PMCID: PMC8836243
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23031397
Selective Boosting of CCR7-Acting Chemokines; Short Peptides Boost Chemokines with Short Basic Tails, Longer Peptides Boost Chemokines with Long Basic Tails
Abstract
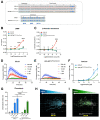
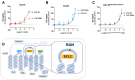
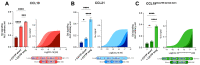
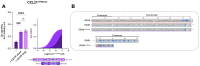
The chemokine receptor CCR7 and its ligands CCL19 and CCL21 regulate the lymph node homing of dendritic cells and naïve T-cells and the following induction of a motile DC-T cell priming state. Although CCL19 and CCL21 bind CCR7 with similar affinities, CCL21 is a weak agonist compared to CCL19. Using a chimeric chemokine, CCL19CCL21N-term|C-term, harboring the N-terminus and the C-terminus of CCL21 attached to the core domain of CCL19, we show that these parts of CCL21 act in a synergistic manner to lower ligand potency and determine the way CCL21 engages with CCR7. We have published that a naturally occurring basic C-terminal fragment of CCL21 (C21TP) boosts the signaling of both CCL19 and CCL21. Boosting occurs as a direct consequence of C21TP binding to the CCR7 N-terminus, which seems to free chemokines with basic C-termini from an unfavorable interaction with negatively charged posttranslational modifications in CCR7. Here, we confirm this using a CCL19-variant lacking the basic C-terminus. This variant displays a 22-fold higher potency at CCR7 compared to WT CCL19 and is highly unaffected by the presence of C21TP. WT CCL19 has a short basic C-terminus, CCL21 a longer one. Here, we propose a way to differentially boost CCL19 and CCL21 activity as short and long versions of C21TP boost CCL19 activity, whereas only a long C21TP version can boost chemokines with a full-length CCL21 C-terminus.
Keywords: CCL19; CCL21; CCR7; basic peptide; biased signaling.
Conflict of interest statement
A.S.J., M.M.R. and G.M.H. are inventors of a patent regarding the use of peptides based on the sequence of the CCL21 C-terminus for use in anti-cancer immunotherapy. F.P. and B.F.V. have ownership interests in Protein Foundry, LLC and XLock Biosciences, LLC. E.P.B., C.K.G., C.V. and M.B.C. have no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The C-terminal peptide of CCL21 drastically augments CCL21 activity through the dendritic cell lymph node homing receptor CCR7 by interaction with the receptor N-terminus.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021 Nov;78(21-22):6963-6978. doi: 10.1007/s00018-021-03930-7. Epub 2021 Sep 29. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021. PMID: 34586443 Free PMC article.
-
Biased Signaling of CCL21 and CCL19 Does Not Rely on N-Terminal Differences, but Markedly on the Chemokine Core Domains and Extracellular Loop 2 of CCR7.Front Immunol. 2019 Sep 13;10:2156. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.02156. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31572374 Free PMC article.
-
Common and biased signaling pathways of the chemokine receptor CCR7 elicited by its ligands CCL19 and CCL21 in leukocytes.J Leukoc Biol. 2016 Jun;99(6):869-82. doi: 10.1189/jlb.2MR0815-380R. Epub 2016 Jan 4. J Leukoc Biol. 2016. PMID: 26729814 Review.
-
CCL19 with CCL21-tail displays enhanced glycosaminoglycan binding with retained chemotactic potency in dendritic cells.J Leukoc Biol. 2018 Aug;104(2):401-411. doi: 10.1002/JLB.2VMA0118-008R. Epub 2018 May 16. J Leukoc Biol. 2018. PMID: 29768676
-
Biased signaling of G protein-coupled receptors - From a chemokine receptor CCR7 perspective.Gen Comp Endocrinol. 2018 Mar 1;258:4-14. doi: 10.1016/j.ygcen.2017.07.004. Epub 2017 Jul 8. Gen Comp Endocrinol. 2018. PMID: 28694053 Review.
Cited by
-
Heparin Specifically Interacts with Basic BBXB Motifs of the Chemokine CCL21 to Define CCR7 Signaling.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jan 14;24(2):1670. doi: 10.3390/ijms24021670. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36675182 Free PMC article.
-
NMR indicates the N-termini of PSGL1 and CCR7 bind competitively to the chemokine CCL21.Biochem Biophys Rep. 2023 Jul 29;35:101524. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrep.2023.101524. eCollection 2023 Sep. Biochem Biophys Rep. 2023. PMID: 37554427 Free PMC article.
-
Chemokine Receptor N-Terminus Charge Dictates Reliance on Post-Translational Modifications for Effective Ligand Capture and Following Boosting by Defense Peptides.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Oct 9;25(19):10854. doi: 10.3390/ijms251910854. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39409188 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

