ARPC1B Is Associated with Lethal Prostate Cancer and Its Inhibition Decreases Cell Invasion and Migration In Vitro
- PMID: 35163398
- PMCID: PMC8836051
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23031476
ARPC1B Is Associated with Lethal Prostate Cancer and Its Inhibition Decreases Cell Invasion and Migration In Vitro
Abstract
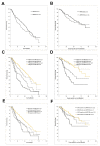
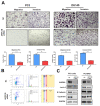
ARPC1B (Actin Related Protein 2/3 Complex Subunit 1B) has been found to be involved in platelet abnormalities of immune-mediated inflammatory disease and eosinophilia. However, its role in prostate cancer (PCa) has not been established. We characterized the role of ARPC1B in PCa invasion and metastasis and investigated its prognosis using in vitro cellular models and PCa clinical data. Higher immunohistochemistry (IHC) expressions of ARPC1B were observed in localized and castrate resistant PCa (CRPC) vs. benign prostate tissue (p < 0.01). Additionally, 47% of patients with grade group 5 (GG) showed high ARPC1B expression vs. other GG patients. Assessing ARPC1B expression in association with two of the common genetic aberrations in PCa (ERG and PTEN) showed significant association to overall and cause-specific survival for combined assessment of ARPC1B and PTEN, and ARPC1B and ERG. Knockdown of ARPC1B impaired the migration and invasion of PC3 and DU145 PCa cells via downregulation of Aurora A kinase (AURKA) and resulted in the arrest of the cells in the G2/M checkpoint of the cell cycle. Additionally, higher ARPC1B expression was observed in stable PC3-ERG cells compared to normal PC3, supporting the association between ERG and ARPC1B. Our findings implicate the role of ARPC1B in PCa invasion and metastasis in association with ERG and further support its prognostic value as a biomarker in association with ERG and PTEN in identifying aggressive phenotypes of PCa cancer.
Keywords: ARPC1B; ERG; PTEN; immigration; invasion; prognosis; prostate cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Kumagai K., Nimura Y., Mizota A., Miyahara N., Aoki M., Furusawa Y., Takiguchi M., Yamamoto S., Seki N. Arpc1b gene is a candidate prediction marker for choroidal malignant melanomas sensitive to radiotherapy. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2006;47:2300–2304. doi: 10.1167/iovs.05-0810. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

