The Regulatory Role of the Central and Peripheral Serotonin Network on Feeding Signals in Metabolic Diseases
- PMID: 35163521
- PMCID: PMC8836087
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23031600
The Regulatory Role of the Central and Peripheral Serotonin Network on Feeding Signals in Metabolic Diseases
Abstract
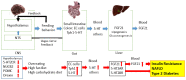
Central and peripheral serotonin (5-hydroxytryptamine, 5-HT) regulate feeding signals for energy metabolism. Disruption of central 5-HT signaling via 5-HT2C receptors (5-HT2CRs) induces leptin-independent hyperphagia in mice, leading to late-onset obesity, insulin resistance, and impaired glucose tolerance. 5-HT2CR mutant mice are more responsive than wild-type mice to a high-fat diet, exhibiting earlier-onset obesity and type 2 diabetes. High-fat and high-carbohydrate diets increase plasma 5-HT and fibroblast growth factor-21 (FGF21) levels. Plasma 5-HT and FGF21 levels are increased in rodents and humans with obesity, type 2 diabetes, and non-alcohol fatty liver diseases (NAFLD). The increases in plasma FGF21 and hepatic FGF21 expression precede hyperinsulinemia, insulin resistance, hyperglycemia, and weight gain in mice fed a high-fat diet. Nutritional, pharmacologic, or genetic inhibition of peripheral 5-HT synthesis via tryptophan hydroxylase 1 (Tph1) decreases hepatic FGF21 expression and plasma FGF21 levels in mice. Thus, perturbing central 5-HT signaling via 5-HT2CRs alters feeding behavior. Increased energy intake via a high-fat diet and/or high-carbohydrate diet can upregulate gut-derived 5-HT synthesis via Tph1. Peripheral 5-HT upregulates hepatic FGF21 expression and plasma FGF21 levels, leading to metabolic diseases such as obesity, insulin resistance, type 2 diabetes, and NAFLD. The 5-HT network in the brain-gut-liver axis regulates feeding signals and may be involved in the development and/or prevention of metabolic diseases.
Keywords: 5-HT2CRs; FGF21; NAFLD; Tph1; energy metabolism; feeding signals; obesity; serotonin; type 2 diabetes.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Whey protein isolate inhibits hepatic FGF21 production, which precedes weight gain, hyperinsulinemia and hyperglycemia in mice fed a high-fat diet.Sci Rep. 2020 Sep 25;10(1):15784. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-72975-8. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32978487 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatic stearoyl CoA desaturase 1 deficiency increases glucose uptake in adipose tissue partially through the PGC-1α-FGF21 axis in mice.J Biol Chem. 2019 Dec 20;294(51):19475-19485. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA119.009868. Epub 2019 Nov 5. J Biol Chem. 2019. PMID: 31690632 Free PMC article.
-
Chronic high-sucrose diet increases fibroblast growth factor 21 production and energy expenditure in mice.J Nutr Biochem. 2017 Nov;49:71-79. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2017.07.010. Epub 2017 Jul 25. J Nutr Biochem. 2017. PMID: 28886439
-
Gut Barrier Proteins Mediate Liver Regulation by the Effects of Serotonin on the Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease.Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2020;21(10):978-984. doi: 10.2174/1389203721666200615171928. Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2020. PMID: 32538722 Review.
-
Nutritional regulation of fibroblast growth factor 21: from macronutrients to bioactive dietary compounds.Horm Mol Biol Clin Investig. 2016 Sep 1;30(1):/j/hmbci.2017.30.issue-1/hmbci-2016-0034/hmbci-2016-0034.xml. doi: 10.1515/hmbci-2016-0034. Horm Mol Biol Clin Investig. 2016. PMID: 27583468 Review.
Cited by
-
Modulation of adipose tissue metabolism by microbial-derived metabolites.Front Microbiol. 2022 Dec 9;13:1031498. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.1031498. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 36569060 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ingestion of whey protein and β-conglycinin exerts opposite effects on intestinal FGF15 and serotonin secretion in mice.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Jan 27;14:1080790. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1080790. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 36777350 Free PMC article.
-
The Influence of Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms On Body Weight Trajectory After Bariatric Surgery: A Systematic Review.Curr Obes Rep. 2023 Sep;12(3):280-307. doi: 10.1007/s13679-023-00514-3. Epub 2023 Jun 30. Curr Obes Rep. 2023. PMID: 37389759
-
Involvement of the liver-gut peripheral neural axis in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease pathologies via hepatic HTR2A.Dis Model Mech. 2022 Jul 1;15(7):dmm049612. doi: 10.1242/dmm.049612. Epub 2022 Jul 26. Dis Model Mech. 2022. PMID: 35765850 Free PMC article.
-
Dysregulated tryptophan metabolism contributes to metabolic syndrome in Chinese community-dwelling older adults.BMC Endocr Disord. 2025 Jan 8;25(1):7. doi: 10.1186/s12902-024-01826-8. BMC Endocr Disord. 2025. PMID: 39780122 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Nonogaki K. Serotonin conflict in sleep-feeding. Vitam. Horm. 2012;89:223–239. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

