Polyamine Oxidase Triggers H2O2-Mediated Spermidine Improved Oxidative Stress Tolerance of Tomato Seedlings Subjected to Saline-Alkaline Stress
- PMID: 35163549
- PMCID: PMC8836047
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23031625
Polyamine Oxidase Triggers H2O2-Mediated Spermidine Improved Oxidative Stress Tolerance of Tomato Seedlings Subjected to Saline-Alkaline Stress
Abstract
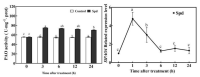
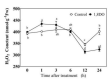
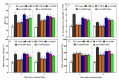
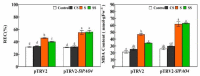
Saline-alkaline stress is one of several major abiotic stresses in crop production. Exogenous spermidine (Spd) can effectively increase tomato saline-alkaline stress resistance by relieving membrane lipid peroxidation damage. However, the mechanism through which exogenous Spd pre-treatment triggers the tomato antioxidant system to resist saline-alkaline stress remains unclear. Whether H2O2 and polyamine oxidase (PAO) are involved in Spd-induced tomato saline-alkaline stress tolerance needs to be determined. Here, we investigated the role of PAO and H2O2 in exogenous Spd-induced tolerance of tomato to saline-alkaline stress. Results showed that Spd application increased the expression and activities of superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase (CAT), ascorbate peroxidase (APX), glutathione reductase (GR), and the ratio of reduced ascorbate (AsA) and glutathione (GSH) contents under saline-alkaline stress condition. Exogenous Spd treatment triggered endogenous H2O2 levels, SlPAO4 gene expression, as well as PAO activity under normal conditions. Inhibiting endogenous PAO activity by 1,8-diaminooctane (1,8-DO, an inhibitor of polyamine oxidase) significantly reduced H2O2 levels in the later stage. Moreover, inhibiting endogenous PAO or silencing the SlPAO4 gene increased the peroxidation damage of tomato leaves under saline-alkaline stress. These findings indicated that exogenous Spd treatment stimulated SlPAO4 gene expression and increased PAO activity, which mediated the elevation of H2O2 level under normal conditions. Consequently, the downstream antioxidant system was activated to eliminate excessive ROS accumulation and relieve membrane lipid peroxidation damage and growth inhibition under saline-alkaline stress. In conclusion, PAO triggered H2O2-mediated Spd-induced increase in the tolerance of tomato to saline-alkaline stress.
Keywords: Solanum lycopersicum; hydrogen peroxide; polyamine oxidase; saline-alkaline stress; spermidine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Spermidine alleviates the growth of saline-stressed ginseng seedlings through antioxidative defense system.Gene. 2014 Mar 1;537(1):70-8. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2013.12.021. Epub 2013 Dec 21. Gene. 2014. PMID: 24365592
-
Spd-CDs-driven respiratory burst oxidase homolog/polyamine oxidase-dependent H2O2 signaling molecule engineering for salt tolerance in tomato.Int J Biol Macromol. 2025 May;306(Pt 4):141680. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2025.141680. Epub 2025 Mar 2. Int J Biol Macromol. 2025. PMID: 40037457
-
Spermidine-mediated hydrogen peroxide signaling enhances the antioxidant capacity of salt-stressed cucumber roots.Plant Physiol Biochem. 2018 Jul;128:152-162. doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2018.05.002. Epub 2018 May 5. Plant Physiol Biochem. 2018. PMID: 29778839
-
Polyamine Oxidase-Generated Reactive Oxygen Species in Plant Development and Adaptation: The Polyamine Oxidase-NADPH Oxidase Nexus.Antioxidants (Basel). 2022 Dec 17;11(12):2488. doi: 10.3390/antiox11122488. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36552696 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of ethylene in ER stress and the unfolded protein response in tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) plants.Plant Physiol Biochem. 2022 Jun 15;181:1-11. doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2022.03.031. Epub 2022 Apr 6. Plant Physiol Biochem. 2022. PMID: 35421744 Review.
Cited by
-
Integrated metabolomic and transcriptomic analysis reveals the role of phenylpropanoid biosynthesis pathway in tomato roots during salt stress.Front Plant Sci. 2022 Dec 8;13:1023696. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.1023696. eCollection 2022. Front Plant Sci. 2022. PMID: 36570882 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Insights into the Synergistic Effects of Putrescine and Ammonium on Dinoflagellates.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jan 21;25(2):1306. doi: 10.3390/ijms25021306. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38279308 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide analysis and expression profiling of the polyamine oxidase gene family in Solanum tuberosum L.BMC Genomics. 2024 Dec 2;25(1):1167. doi: 10.1186/s12864-024-10992-x. BMC Genomics. 2024. PMID: 39623364 Free PMC article.
-
Exogenous menadione sodium bisulphite alleviates detrimental effects of alkaline stress on wheat (Triticum aestivum L.).Physiol Mol Biol Plants. 2022 Oct;28(10):1889-1903. doi: 10.1007/s12298-022-01250-z. Epub 2022 Nov 20. Physiol Mol Biol Plants. 2022. PMID: 36484028 Free PMC article.
-
A role for aquaporins in the modulation of cold stress tolerance in oriental melon.Plant Physiol. 2024 Dec 23;197(1):kiae578. doi: 10.1093/plphys/kiae578. Plant Physiol. 2024. PMID: 39484985 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Shu S., Yuan R.N., Shen J.L., Chen J., Wang L.J., Wu J.Q., Sun J., Wang Y., Guo S.R. The positive regulation of putrescine on light-harvesting complex II and excitation energy dissipation in salt-stressed cucumber seedlings. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2019;162:283–294. doi: 10.1016/j.envexpbot.2019.02.027. - DOI
-
- Li X., Li Y., Ahammed G.J., Zhang X.N., Ying L., Zhang L., Yan P., Zhang L.P., Li Q.Y., Han W.Y. RBOH1-dependent apoplastic H2O2 mediates epigallocatechin-3-gallate-induced abiotic stress tolerance in Solanum lycopersicum L. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2019;161:357–366. doi: 10.1016/j.envexpbot.2018.11.013. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

