To Be or Not to Be: The Divergent Action and Metabolism of Sphingosine-1 Phosphate in Pancreatic Beta-Cells in Response to Cytokines and Fatty Acids
- PMID: 35163559
- PMCID: PMC8835924
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23031638
To Be or Not to Be: The Divergent Action and Metabolism of Sphingosine-1 Phosphate in Pancreatic Beta-Cells in Response to Cytokines and Fatty Acids
Abstract
Sphingosine-1 phosphate (S1P) is a bioactive sphingolipid with multiple functions conveyed by the activation of cell surface receptors and/or intracellular mediators. A growing body of evidence indicates its important role in pancreatic insulin-secreting beta-cells that are necessary for maintenance of glucose homeostasis. The dysfunction and/or death of beta-cells lead to diabetes development. Diabetes is a serious public health burden with incidence growing rapidly in recent decades. The two major types of diabetes are the autoimmune-mediated type 1 diabetes (T1DM) and the metabolic stress-related type 2 diabetes (T2DM). Despite many differences in the development, both types of diabetes are characterized by chronic hyperglycemia and inflammation. The inflammatory component of diabetes remains under-characterized. Recent years have brought new insights into the possible mechanism involved in the increased inflammatory response, suggesting that environmental factors such as a westernized diet may participate in this process. Dietary lipids, particularly palmitate, are substrates for the biosynthesis of bioactive sphingolipids. Disturbed serum sphingolipid profiles were observed in both T1DM and T2DM patients. Many polymorphisms were identified in genes encoding enzymes of the sphingolipid pathway, including sphingosine kinase 2 (SK2), the S1P generating enzyme which is highly expressed in beta-cells. Proinflammatory cytokines and free fatty acids have been shown to modulate the expression and activity of S1P-generating and S1P-catabolizing enzymes. In this review, the similarities and differences in the action of extracellular and intracellular S1P in beta-cells exposed to cytokines or free fatty acids will be identified and the outlook for future research will be discussed.
Keywords: beta-cells; cytokines; free fatty acids; inflammation; lipotoxicity; sphingolipids; sphingosine-1 phosphate; type 1 diabetes; type 2 diabetes.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares no conflict of interest.
Figures
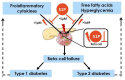
Similar articles
-
Sphingosine 1-phosphate counteracts insulin signaling in pancreatic β-cells via the sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor subtype 2.FASEB J. 2015 Aug;29(8):3357-69. doi: 10.1096/fj.14-263194. Epub 2015 Apr 24. FASEB J. 2015. PMID: 25911610
-
Sphingosine 1-phosphate (S1P) regulates glucose-stimulated insulin secretion in pancreatic beta cells.J Biol Chem. 2012 Apr 13;287(16):13457-64. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.268185. Epub 2012 Mar 2. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22389505 Free PMC article.
-
Sphingosine 1-phosphate metabolism and insulin signaling.Cell Signal. 2021 Jun;82:109959. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2021.109959. Epub 2021 Feb 22. Cell Signal. 2021. PMID: 33631318 Review.
-
Sphingosine-1 Phosphate Lyase Regulates Sensitivity of Pancreatic Beta-Cells to Lipotoxicity.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Oct 8;22(19):10893. doi: 10.3390/ijms221910893. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34639233 Free PMC article.
-
Sphingosine-1-Phosphate Metabolism in the Regulation of Obesity/Type 2 Diabetes.Cells. 2020 Jul 13;9(7):1682. doi: 10.3390/cells9071682. Cells. 2020. PMID: 32668665 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The emerging roles of sphingosine 1-phosphate and SphK1 in cancer resistance: a promising therapeutic target.Cancer Cell Int. 2024 Feb 28;24(1):89. doi: 10.1186/s12935-024-03221-8. Cancer Cell Int. 2024. PMID: 38419070 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sphingosine 1-phosphate lyase facilitates cancer progression through converting sphingolipids to glycerophospholipids.Clin Transl Med. 2022 Sep;12(9):e1056. doi: 10.1002/ctm2.1056. Clin Transl Med. 2022. PMID: 36125914 Free PMC article.
-
Mitochondrial oxidative damage reprograms lipid metabolism of renal tubular epithelial cells in the diabetic kidney.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2024 Jan 11;81(1):23. doi: 10.1007/s00018-023-05078-y. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2024. PMID: 38200266 Free PMC article.
-
Lipid metabolism in type 1 diabetes mellitus: Pathogenetic and therapeutic implications.Front Immunol. 2022 Oct 6;13:999108. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.999108. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36275658 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

