Antitumor Effect of Regorafenib on MicroRNA Expression in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cell Lines
- PMID: 35163589
- PMCID: PMC8835935
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23031667
Antitumor Effect of Regorafenib on MicroRNA Expression in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cell Lines
Abstract
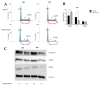
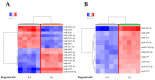
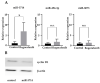
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the most common primary malignancy of the liver and is one of the leading causes of cancer-related deaths worldwide. Regorafenib, a multi-kinase inhibitor, is used as a second-line treatment for advanced HCC. Here, we aimed to investigate the mechanism of the antitumor effect of regorafenib on HCC and evaluate altered microRNA (miRNA) expression. Cell proliferation was examined in six HCC cell lines (HuH-7, HepG2, HLF, PLC/PRF/5, Hep3B, and Li-7) using the Cell Counting Kit-8 assay. Xenografted mouse models were used to assess the effects of regorafenib in vivo. Cell cycle analysis, western blotting analysis, and miRNA expression analysis were performed to identify the antitumor inhibitory potential of regorafenib on HCC cells. Regorafenib suppressed proliferation in HuH-7 cell and induced G0/G1 cell cycle arrest and cyclin D1 downregulation in regorafenib-sensitive cells. During miRNA analysis, miRNA molecules associated with the antitumor effect of regorafenib were found. Regorafenib suppresses cell proliferation and tumor growth in HCC by decreasing cyclin D1 via alterations in intracellular and exosomal miRNAs in HCC.
Keywords: antitumor effect; cell cycle; cell proliferation; cyclin; hepatocellular carcinoma; microRNA; regorafenib.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors disclose no potential conflict of interest.
Figures



References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

