SGLT2 Inhibitors and Their Antiarrhythmic Properties
- PMID: 35163599
- PMCID: PMC8835896
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23031678
SGLT2 Inhibitors and Their Antiarrhythmic Properties
Abstract
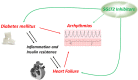
Sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors are gaining ground as standard therapy for heart failure with a class-I recommendation in the recently updated heart failure guidelines from the European Society of Cardiology. Different gliflozins have shown impressive beneficial effects in patients with and without diabetes mellitus type 2, especially in reducing the rates for hospitalization for heart failure, yet little is known on their antiarrhythmic properties. Atrial and ventricular arrhythmias were reported by clinical outcome trials with SGLT2 inhibitors as adverse events, and SGLT2 inhibitors seemed to reduce the rate of arrhythmias compared to placebo treatment in those trials. Mechanistical links are mainly unrevealed, since hardly any experiments investigated their impact on arrhythmias. Prospective trials are currently ongoing, but no results have been published so far. Arrhythmias are common in the heart failure population, therefore the understanding of possible interactions with SGLT2 inhibitors is crucial. This review summarizes evidence from clinical data as well as the sparse experimental data of SGLT2 inhibitors and their effects on arrhythmias.
Keywords: SGLT2 inhibitors; arrhythmias; atrial fibrillation; ventricular arrhythmias.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors are investigators of the ERASE-trial, otherwise no conflict of interest is declared.
Figures

References
-
- Writing C. 2021 Update to the 2017 ACC expert consensus decision pathway for optimization of heart failure treatment: Answers to 10 pivotal issues about heart failure with reduced ejection fraction: A report of the American College of Cardiology solution set oversight committee. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2021;77:772–810. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

