The Therapeutic Prospects of Targeting IL-1R1 for the Modulation of Neuroinflammation in Central Nervous System Disorders
- PMID: 35163653
- PMCID: PMC8915186
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23031731
The Therapeutic Prospects of Targeting IL-1R1 for the Modulation of Neuroinflammation in Central Nervous System Disorders
Abstract
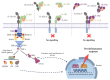
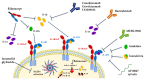
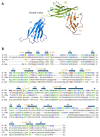
The interleukin-1 receptor type 1 (IL-1R1) holds pivotal roles in the immune system, as it is positioned at the "epicenter" of the inflammatory signaling networks. Increased levels of the cytokine IL-1 are a recognized feature of the immune response in the central nervous system (CNS) during injury and disease, i.e., neuroinflammation. Despite IL-1/IL-1R1 signaling within the CNS having been the subject of several studies, the roles of IL-1R1 in the CNS cellular milieu still cause controversy. Without much doubt, however, the persistent activation of the IL-1/IL-1R1 signaling pathway is intimately linked with the pathogenesis of a plethora of CNS disease states, ranging from Alzheimer's disease (AD), Parkinson's disease (PD), amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) and multiple sclerosis (MS), all the way to schizophrenia and prion diseases. Importantly, a growing body of evidence is showing that blocking IL-1R1 signaling via pharmacological or genetic means in different experimental models of said CNS diseases leads to reduced neuroinflammation and delayed disease progression. The aim of this paper is to review the recent progress in the study of the biological roles of IL-1R1, as well as to highlight key aspects that render IL-1R1 a promising target for the development of novel disease-modifying treatments for multiple CNS indications.
Keywords: CNS diseases; interleukin-1; interleukin-1 receptor type 1; neuroinflammation; therapeutic target.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. This review was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Fantuzzi G. Body Messages. Harvard University Press; Cambridge, MA, USA: 2016. 3. Evolution of message discovery: The Interleukin-1 family; pp. 29–73.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

