5'RNA Trans-Splicing Repair of COL7A1 Mutant Transcripts in Epidermolysis Bullosa
- PMID: 35163654
- PMCID: PMC8835740
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23031732
5'RNA Trans-Splicing Repair of COL7A1 Mutant Transcripts in Epidermolysis Bullosa
Abstract
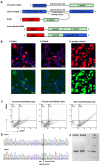
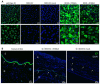
Mutations within the COL7A1 gene underlie the inherited recessive subtype of the blistering skin disease dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa (RDEB). Although gene replacement approaches for genodermatoses are clinically advanced, their implementation for RDEB is challenging and requires endogenous regulation of transgene expression. Thus, we are using spliceosome-mediated RNA trans-splicing (SMaRT) to repair mutations in COL7A1 at the mRNA level. Here, we demonstrate the capability of a COL7A1-specific RNA trans-splicing molecule (RTM), initially selected using a fluorescence-based screening procedure, to accurately replace COL7A1 exons 1 to 64 in an endogenous setting. Retroviral RTM transduction into patient-derived, immortalized keratinocytes resulted in an increase in wild-type transcript and protein levels, respectively. Furthermore, we revealed accurate deposition of recovered type VII collagen protein within the basement membrane zone of expanded skin equivalents using immunofluorescence staining. In summary, we showed for the first time the potential of endogenous 5' trans-splicing to correct pathogenic mutations within the COL7A1 gene. Therefore, we consider 5' RNA trans-splicing a suitable tool to beneficially modulate the RDEB-phenotype, thus targeting an urgent need of this patient population.
Keywords: COL7A1; RNA therapy; RNA trans-splicing; epidermolysis bullosa.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
COL7A1 Editing via RNA Trans-Splicing in RDEB-Derived Skin Equivalents.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Feb 22;24(5):4341. doi: 10.3390/ijms24054341. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36901775 Free PMC article.
-
Construction and validation of an RNA trans-splicing molecule suitable to repair a large number of COL7A1 mutations.Gene Ther. 2016 Nov;23(11):775-784. doi: 10.1038/gt.2016.57. Epub 2016 Aug 11. Gene Ther. 2016. PMID: 27434145 Free PMC article.
-
Trans-splicing improvement by the combined application of antisense strategies.Int J Mol Sci. 2015 Jan 6;16(1):1179-91. doi: 10.3390/ijms16011179. Int J Mol Sci. 2015. PMID: 25569093 Free PMC article.
-
Mutation analysis and characterization of COL7A1 mutations in dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa.Exp Dermatol. 2008 Jul;17(7):553-68. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0625.2008.00723.x. Exp Dermatol. 2008. PMID: 18558993 Review.
-
Review of collagen VII sequence variants found in Australasian patients with dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa reveals nine novel COL7A1 variants.J Dermatol Sci. 2007 Jun;46(3):169-78. doi: 10.1016/j.jdermsci.2007.02.006. Epub 2007 Apr 10. J Dermatol Sci. 2007. PMID: 17425959 Review.
Cited by
-
Diverse clinical and genetic characteristics of six cases of inherited epidermolysis bullosa.Exp Ther Med. 2022 Oct 21;24(6):727. doi: 10.3892/etm.2022.11663. eCollection 2022 Dec. Exp Ther Med. 2022. PMID: 36340603 Free PMC article.
-
Innovations in the Treatment of Dystrophic Epidermolysis Bullosa (DEB): Current Landscape and Prospects.Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2023 Jun 14;19:455-473. doi: 10.2147/TCRM.S386923. eCollection 2023. Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2023. PMID: 37337559 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RNA exon editing: Splicing the way to treat human diseases.Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2024 Aug 16;35(3):102311. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2024.102311. eCollection 2024 Sep 10. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2024. PMID: 39281698 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular Research and Treatment of Skin Diseases.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 May 13;23(10):5435. doi: 10.3390/ijms23105435. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35628246 Free PMC article.
-
COL7A1 Editing via RNA Trans-Splicing in RDEB-Derived Skin Equivalents.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Feb 22;24(5):4341. doi: 10.3390/ijms24054341. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36901775 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Has C., Bauer J.W., Bodemer C., Bolling M.C., Bruckner-Tuderman L., Diem A., Fine J.-D., Heagerty A., Hovnanian A., Marinkovich M.P., et al. Consensus reclassification of inherited epidermolysis bullosa and other disorders with skin fragility. Br. J. Dermatol. 2020;183:614–627. doi: 10.1111/bjd.18921. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Fine J.D., Bruckner-Tuderman L., Eady R.A.J., Bauer E.A., Bauer J.W., Has C., Heagerty A., Hintner H., Hovnanian A., Jonkman M.F., et al. Inherited epidermolysis bullosa: Updated recommendations on diagnosis and classification. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology. 2014;70:1103–1126. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2014.01.903. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

