Hedgehog Pathway Inhibitors as Targeted Cancer Therapy and Strategies to Overcome Drug Resistance
- PMID: 35163655
- PMCID: PMC8835893
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23031733
Hedgehog Pathway Inhibitors as Targeted Cancer Therapy and Strategies to Overcome Drug Resistance
Abstract
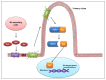
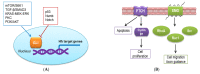
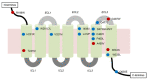
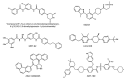
Hedgehog (Hh) signaling is a highly conserved pathway that plays a vital role during embryonic development. Recently, uncontrolled activation of this pathway has been demonstrated in various types of cancer. Therefore, Hh pathway inhibitors have emerged as an important class of anti-cancer agents. Unfortunately, however, their reputation has been tarnished by the emergence of resistance during therapy, necessitating clarification of mechanisms underlying the drug resistance. In this review, we briefly overview canonical and non-canonical Hh pathways and their inhibitors as targeted cancer therapy. In addition, we summarize the mechanisms of resistance to Smoothened (SMO) inhibitors, including point mutations of the drug binding pocket or downstream molecules of SMO, and non-canonical mechanisms to reinforce Hh pathway output. A distinct mechanism involving loss of primary cilia is also described to maintain GLI activity in resistant tumors. Finally, we address the main strategies to circumvent the drug resistance. These strategies include the development of novel and potent inhibitors targeting different components of the canonical Hh pathway or signaling molecules of the non-canonical pathway. Further studies are necessary to avoid emerging resistance to Hh inhibitors and establish an optimal customized regimen with improved therapeutic efficacy to treat various types of cancer, including basal cell carcinoma.
Keywords: basal cell carcinoma; drug resistance; hedgehog inhibitor; hedgehog signaling; smoothened inhibitor; targeted cancer therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Targeting the Hedgehog signaling pathway in cancer: beyond Smoothened.Oncotarget. 2015 Jun 10;6(16):13899-913. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.4224. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 26053182 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting class I histone deacetylases by the novel small molecule inhibitor 4SC-202 blocks oncogenic hedgehog-GLI signaling and overcomes smoothened inhibitor resistance.Int J Cancer. 2018 Mar 1;142(5):968-975. doi: 10.1002/ijc.31117. Epub 2017 Nov 6. Int J Cancer. 2018. PMID: 29055107 Free PMC article.
-
Current trends in Hedgehog signaling pathway inhibition by small molecules.Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2018 Oct 15;28(19):3131-3140. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2018.08.033. Epub 2018 Aug 27. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2018. PMID: 30177379 Review.
-
Non-canonical Hedgehog Signaling Pathway in Cancer: Activation of GLI Transcription Factors Beyond Smoothened.Front Genet. 2019 Jun 12;10:556. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2019.00556. eCollection 2019. Front Genet. 2019. PMID: 31244888 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The utility of hedgehog signaling pathway inhibition for cancer.Oncologist. 2012;17(8):1090-9. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.2011-0450. Epub 2012 Jul 31. Oncologist. 2012. PMID: 22851551 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Ornidazole suppresses CD133+ melanoma stem cells via inhibiting hedgehog signaling pathway and inducing multiple death pathways in a mouse model.Croat Med J. 2022 Oct 31;63(5):461-474. doi: 10.3325/cmj.2022.63.461. Croat Med J. 2022. PMID: 36325671 Free PMC article.
-
NF-κB signaling pathway in osteosarcoma: from signaling networks to targeted therapy.Front Oncol. 2025 Jul 25;15:1565760. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1565760. eCollection 2025. Front Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40786506 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The PROTAC selectively degrading Bcl-xL represents a novel Hedgehog pathway inhibitor with capacity of combating resistance to Smoothened inhibitors while sparing bone growth.Theranostics. 2022 Oct 24;12(17):7476-7490. doi: 10.7150/thno.75421. eCollection 2022. Theranostics. 2022. PMID: 36438482 Free PMC article.
-
CRISPR/Cas9-mediated silencing of CD44: unveiling the role of hyaluronic acid-mediated interactions in cancer drug resistance.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2024 May;397(5):2849-2876. doi: 10.1007/s00210-023-02840-8. Epub 2023 Nov 22. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 37991544 Review.
-
Sonic Hedgehog Promotes Proliferation and Migration of Fibroblast-Like Synoviocytes in Rheumatoid Arthritis via Rho/ROCK Signaling.J Immunol Res. 2022 Jun 22;2022:3423692. doi: 10.1155/2022/3423692. eCollection 2022. J Immunol Res. 2022. PMID: 35785032 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

