Optogenetic and Chemical Induction Systems for Regulation of Transgene Expression in Plants: Use in Basic and Applied Research
- PMID: 35163658
- PMCID: PMC8835832
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23031737
Optogenetic and Chemical Induction Systems for Regulation of Transgene Expression in Plants: Use in Basic and Applied Research
Abstract
Continuous and ubiquitous expression of foreign genes sometimes results in harmful effects on the growth, development and metabolic activities of plants. Tissue-specific promoters help to overcome this disadvantage, but do not allow one to precisely control transgene expression over time. Thus, inducible transgene expression systems have obvious benefits. In plants, transcriptional regulation is usually driven by chemical agents under the control of chemically-inducible promoters. These systems are diverse, but usually contain two elements, the chimeric transcription factor and the reporter gene. The commonly used chemically-induced expression systems are tetracycline-, steroid-, insecticide-, copper-, and ethanol-regulated. Unlike chemical-inducible systems, optogenetic tools enable spatiotemporal, quantitative and reversible control over transgene expression with light, overcoming limitations of chemically-inducible systems. This review updates and summarizes optogenetic and chemical induction methods of transgene expression used in basic plant research and discusses their potential in field applications.
Keywords: agriculture; chemical induction; optogenetics; plants; transgene expression regulation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures


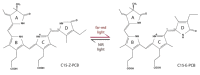
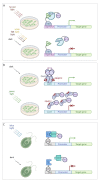
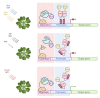

Similar articles
-
Optogenetic control of gene expression in plants in the presence of ambient white light.Nat Methods. 2020 Jul;17(7):717-725. doi: 10.1038/s41592-020-0868-y. Epub 2020 Jun 29. Nat Methods. 2020. PMID: 32601426
-
A Green-Light-Responsive System for the Control of Transgene Expression in Mammalian and Plant Cells.ACS Synth Biol. 2018 May 18;7(5):1349-1358. doi: 10.1021/acssynbio.7b00450. Epub 2018 Apr 19. ACS Synth Biol. 2018. PMID: 29634242
-
Chemical-inducible systems for regulated expression of plant genes.Curr Opin Biotechnol. 2000 Apr;11(2):146-51. doi: 10.1016/s0958-1669(00)00073-2. Curr Opin Biotechnol. 2000. PMID: 10753773 Review.
-
An optogenetic upgrade for the Tet-OFF system.Biotechnol Bioeng. 2015 Jul;112(7):1483-7. doi: 10.1002/bit.25562. Epub 2015 Mar 13. Biotechnol Bioeng. 2015. PMID: 25683779
-
Chemically regulated gene expression in plants.Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2003 Apr;6(2):169-77. doi: 10.1016/s1369-5266(03)00005-0. Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2003. PMID: 12667875 Review.
Cited by
-
Systems for Targeted Silencing of Gene Expression and Their Application in Plants and Animals.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 May 11;25(10):5231. doi: 10.3390/ijms25105231. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38791270 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Live-cell imaging of a plant virus replicase during infection using a genetically encoded, antibody-based probe.Plant Physiol. 2025 May 30;198(2):kiaf240. doi: 10.1093/plphys/kiaf240. Plant Physiol. 2025. PMID: 40479561 Free PMC article.
-
How to use CRISPR/Cas9 in plants: from target site selection to DNA repair.J Exp Bot. 2024 Sep 11;75(17):5325-5343. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erae147. J Exp Bot. 2024. PMID: 38648173 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Synthetic microbe-to-plant communication channels.Nat Commun. 2024 Feb 28;15(1):1817. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-45897-6. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 38418817 Free PMC article.
-
Plant Biology and Biotechnology: Focus on Genomics and Bioinformatics.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jun 17;23(12):6759. doi: 10.3390/ijms23126759. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35743200 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chen L., Yang H., Fang Y., Guo W., Chen H., Zhang X., Dai W., Chen S., Hao Q., Yuan S., et al. Overexpression of GmMYB14 improves high-density yield and drought tolerance of soybean through regulating plant architecture mediated by the brassinosteroid pathway. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2021;19:702–716. doi: 10.1111/pbi.13496. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Fuganti-Pagliarini R., Ferreira L.C., Rodrigues F.A., Molinari H.B.C., Marin S.R.R., Molinari M.D.C., Marcolino-Gomes J., Mertz-Henning L.M., Farias J.R.B., de Oliveira M.C.N., et al. Characterization of soybean genetically modified for drought tolerance in field conditions. Front. Plant Sci. 2017;8:448. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2017.00448. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

