Structural Analysis of Human Serum Albumin in Complex with the Fibrate Drug Gemfibrozil
- PMID: 35163693
- PMCID: PMC8836495
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23031769
Structural Analysis of Human Serum Albumin in Complex with the Fibrate Drug Gemfibrozil
Abstract
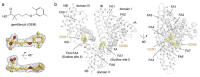
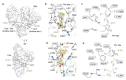
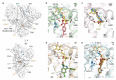
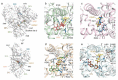
Gemfibrozil (GEM) is an orally administered lipid-regulating fibrate derivative drug sold under the brand name Lopid®, among others. Since its approval in the early 80s, GEM has been largely applied to treat hypertriglyceridemia and other disorders of lipid metabolism. Though generally well tolerated, GEM can alter the distribution and the free, active concentration of some co-administered drugs, leading to adverse effects. Most of them appear to be related to the ability of GEM to bind with high affinity human serum albumin (HSA), the major drug-carrier protein in blood plasma. Here, we report the crystal structure of HSA in complex with GEM. Two binding sites have been identified, namely Sudlow's binding sites I (FA7) and II (FA3-FA4). A comparison of the crystal structure of HSA in complex with GEM with those of other previously described HSA-drug complexes enabled us to appreciate the analogies and differences in their respective binding modes. The elucidation of the molecular interaction between GEM and HSA might offer the basis for the development of novel GEM derivatives that can be safely and synergistically co-administered with other drugs, enabling augmented therapeutic efficacies.
Keywords: Lopid; Sudlow’s site; fibrate; fibric acid; gemfibrozil; hypercholesterolemia; hyperlipidaemia; hypertriglyceridemia; hypolipidemic drug; serum albumin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures

Similar articles
-
NMR and Docking Calculations Reveal Novel Atomistic Selectivity of a Synthetic High-Affinity Free Fatty Acid vs. Free Fatty Acids in Sudlow's Drug Binding Sites in Human Serum Albumin.Molecules. 2023 Dec 7;28(24):7991. doi: 10.3390/molecules28247991. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 38138481 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Basis for the Selectivity of DHA and EPA in Sudlow's Drug Binding Sites in Human Serum Albumin with the Combined Use of NMR and Docking Calculations.Molecules. 2023 Apr 26;28(9):3724. doi: 10.3390/molecules28093724. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37175134 Free PMC article.
-
Perfluoroalkane sulfonyl fluorides non-covalently bind to human serum albumin at Sudlow's sites.Toxicol Lett. 2019 Feb;301:17-23. doi: 10.1016/j.toxlet.2018.11.001. Epub 2018 Nov 5. Toxicol Lett. 2019. PMID: 30408508
-
Effects of gemfibrozil and other fibric acid derivatives on blood lipids and lipoproteins.J Clin Pharmacol. 1991 Jan;31(1):25-37. doi: 10.1002/j.1552-4604.1991.tb01883.x. J Clin Pharmacol. 1991. PMID: 2045526 Review.
-
Displacement of Drugs from Human Serum Albumin: From Molecular Interactions to Clinical Significance.Curr Med Chem. 2017;24(18):1930-1947. doi: 10.2174/0929867324666170202152134. Curr Med Chem. 2017. PMID: 28155602 Review.
Cited by
-
Ultraviolet Resonance Raman Spectra of Serum Albumins.Appl Spectrosc. 2023 Sep;77(9):1044-1052. doi: 10.1177/00037028231183728. Epub 2023 Jul 7. Appl Spectrosc. 2023. PMID: 37415516 Free PMC article.
-
Investigation of the Interaction between Human Serum Albumin and Branched Short-Chain Perfluoroalkyl Compounds.Chem Res Toxicol. 2022 Nov 21;35(11):2049-2058. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrestox.2c00211. Epub 2022 Sep 23. Chem Res Toxicol. 2022. PMID: 36148994 Free PMC article.
-
A facile synthesis of 2-(4-((4-chlorophenyl)(hydroxy)methyl) phenoxy)-2-methylpropanoic acid: Metabolite of anti-hyperlipidemic drug Fenofibrate.Results Chem. 2024 Jan;7:101282. doi: 10.1016/j.rechem.2023.101282. Epub 2023 Dec 23. Results Chem. 2024. PMID: 39086552 Free PMC article.
-
Human Serum Albumin: From Molecular Aspects to Biotechnological Applications.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Feb 17;24(4):4081. doi: 10.3390/ijms24044081. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36835490 Free PMC article.
-
Displacing the Burden: A Review of Protein-Bound Uremic Toxin Clearance Strategies in Chronic Kidney Disease.J Clin Med. 2024 Mar 1;13(5):1428. doi: 10.3390/jcm13051428. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 38592263 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hermens W.A.J.J., Lohman J.J.H.M. Gemfibrozil (Lopid®) Pharm. Weekbl. 1990;125:984–986.
-
- Kundu S.C., Roxy S., Batabyal S.K. Gemfibrozil in dyslipidaemia. J. Assoc. Physicians India. 1990;38:156–159. - PubMed
-
- Gaw A., Packard C.J., Shepherd J. In: Fibrates-Principles and Treatment of Lipoprotein Disorders. Schettler G., Habenicht A.J.R., editors. Springer; Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany: 1994. pp. 325–348.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

